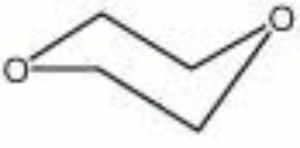
Dioxane
Description
A toxic, colorless liquid with a slight ether-like smell. Dioxane is no longer recommended for use. In the past, it was used as a solvent for acetate cellulose acetate, cellulose ethyl cellulose, cellulose benzyl cellulose, and other resins, oils, and waxes. It was often found in paint and varnish removers. Dioxane was also used as a surfactant and dispersant in textile processing, dyeing, and printing.
Synonyms and Related Terms
diethylene oxide; dioxyethylene ether; 1,4-diethylene dioxide; diethylene ether; 1,4-dioxane
Other Properties
Miscible in water and most organic solvents.
| Composition | C4H8O2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 123-91-1 |
| Melting Point | 11.8 |
| Density | 1.0329 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 88.1 |
| Refractive Index | 1.420 |
| Boiling Point | 101.1 |
Hazards and Safety
Highly toxic by skin contact, inhalation, and ingestion. Suspected carcinogen. Fumes are highly flammable and explosive. Flash point = 12C (54F)
LINK: International Chemical Safety Card
Authority
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Hermann Kuhn, Hermann Kuhn, Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities, Butterworths, London, 1986
- Michael McCann, Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: ref. index = 1.420