Egyptian blue
Description
A synthetic inorganic pigment composed of a double silicate of calcium and copper. Egyptian blue is prepared by heating a mixture of silica, copper salts, and calcite in a carbonate sodium carbonate flux to 830 C. This forms a stable blue frit that usually contains some calcite and silica as impurities. Egyptian blue was used by the Egyptians over 5000 years ago as a pottery glaze and as a watercolor pigment in wall paintings. The colorfast pigment has coarse, irregular particles and ranges in color from a powdery blue to a royal blue. Similar materials, later manufactured in Italy and called Pompeian blue and Pozzuoli blue, have similar chemical compositions and optical properties. Egyptian blue is stable in all types of media and is unaffected by acids or alkali.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Pompeian blue; Pigment Blue 31; CI 77437; cuprorivaite (mineral); azul egipcio (Esp.); bleu gyptien (Fr.); bleu d'Alexandrie (Fr.); gyptisch Blau (Deut.); Frittenblau (Deut.); Pompejanischblau (Deut.); aigyptiako mple (Gr.); blu egiziano (It.); azzurro pompeiano (It.); fritta blue (It.); fritta egiziana (It.); Egyptisch blauw (Ned.); azul Egpcio (Port.); egyptinsininen (Fin.); lomentum (Lat.) puteolanum (Pliny); irtiu (Egypt.); gyptischblau (Deut.); Pozzuoli blue; Alexandria blue; blue frit; Vestorian blue; Italian blue; copper frit; Venetian blue;
Other Properties
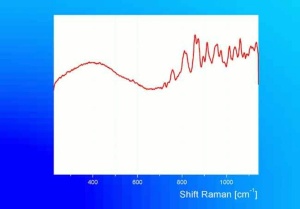
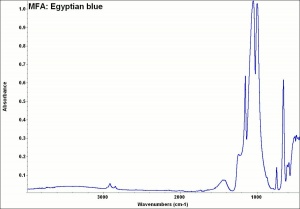
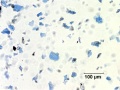
Irregular particle shapes. Strong birefringence. Pleochroic from deep blue to colorless. Appears red with Chelsea filter. Ancient Egyptian blue may contain quartz and calcite as impurities.
Insoluble in acids. Unaffected by light or heat.
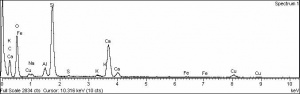
| Composition | CaCuSi4O10 |
|---|---|
| Refractive Index | e =1.59, w =1.63 |
Additional Information
J.Riederer, "Egyptian Blue", Artists Pigments, Volume 3, E. West FitzHugh (ed.), Oxford University Press: Oxford, 1997. Pigments Through the Ages: Egyptian blue
Comparisons
Characteristics of Common Blue Pigments
Additional Images
Authority
- Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, Pigment Compendium, Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004
- The Dictionary of Art, Grove's Dictionaries Inc., New York, 1996 Comment: 'Pigment'
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: ref index=1.605;1.635
- G.S.Brady, G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 611
- Ralph Mayer, Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Monona Rossol, Monona Rossol, The Artist's Complete Health and Safety Guide, Allworth Press, New York, 1994
- Thomas B. Brill, Thomas B. Brill, Light Its Interaction with Art and Antiquities, Plenum Press, New York City, 1980
- Website address 2 Comment: http://www.coloria.net/varita.htm - foreign language equivalent terms
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000
- Website address 1, Website address 1 Comment: Pigments Through the Ages - http://webexhibits.org/pigments/indiv/overview/egyptblue.html - e=1.59, w =1.633