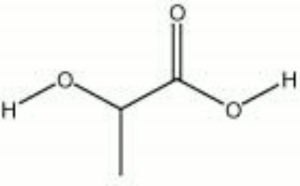
Lactic acid
Description
A thick water-soluble liquid that occurs naturally in sour milk. Lactic acid is also found in fermented molasses, apples, tomato juice, beer, and wine. It is formed by the action of Bacillus acidilacti on glucose, sucrose, and lactose. Lactic acid is used in dyeing vats as a mordant for wools and as a solvent for water-insoluble dyes. It is also used in leather processing.
Synonyms and Related Terms
milk acid; alpha-hydroxypropionic acid; DL-lactic acid; 2-hydroxypropanoic acid
Other Properties
Soluble in water, ethanol, glycerol, furfural. Slightly soluble in ether. Insoluble in chloroform, petroleum ether and carbon disulfide.
| Composition | CH3CH2OCOOH |
|---|---|
| CAS | 50-21-5 |
| Melting Point | 18 |
| Density | 1.2 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 90.1 |
| Boiling Point | 122 |
Hazards and Safety
Combustible. Flash point = 110 C
Medium strength acid. Contact may cause redness or burns.
LINK: International Chemical Safety Card
Authority
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 4059
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985