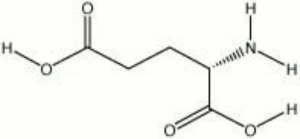
Glutamic acid
Description
A naturally occurring, non-essential amino acid found in wheat gluten, vegetable products, and animals. Glutamic acid was first isolated in 1865. The body synthesizes glutamic acid during carbohydrate metabolism. Glutamic acid also occurs in many plants. It is a very polar molecule that plays the role of an excitatory amino acid (EAA) in neurotransmission.
Synonyms and Related Terms
GLU: glutamininc acid; alpha-aminoglutaric acid; 2-amino pentanedioic acid; glutaminol; glutaton; glutamate (anionic form); Glutaminsäure (Deut.); glutamato (Esp.); ácido glutámico (Esp.); acide glutamique (Fr.); acido glutammico (It.); glutamaat (Ned.); kwas glutaminowy (Pol.); glutaminsyra (Sven.)
Other Properties
Soluble in water. Insoluble in ether, ethanol, acetone and acetic acid.
| Composition | C5H9NO4 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 56-86-0 |
| Melting Point | 160-249 |
| Density | 1.538 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 147.13 |
| Refractive Index | 1.538 |
Hazards and Safety
Mallinckrodt Baker: MSDS
Authority
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 4477 has melting point=160C
- MSDS Sheet Comment: Mallinckrodt Baker: - has melting point = 205C
- Website address 1 Comment: Olympus Microscopy Resource Center at http://www.olympusmicro.com/galleries/polarizedlight/pages/glutamicacidsmall.html
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glutamic_acid (Accessed Nov. 2, 2005) - has melting point=247-249 C