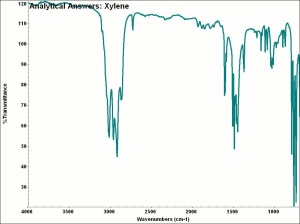
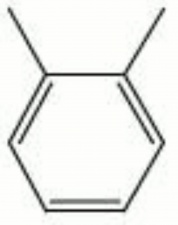
Xylenes
Description
A clear, oily, colorless mixture of three liquid isomers: ortho-, meta- and para-xylene. Xylenes are obtained from coal-tar distillation with the meta- isomer being predominate. A large quantity of xylenes are used annually as raw or intermediate materials for synthetic fibers and plastics such as polyester. Xylenes are more toxic than toluene but safer than benzene. Xylene is used as a solvent for alkyd resins, synthetic lacquers, organic enamels, and rubber cements. It is also used in dye manufacture, as an aviation fuel, and in Canada balsam for oil-immersion microscopy.
Synonyms and Related Terms
xylene; xylol; dimethylbenzene; aromatic naphtha; ortho-xylene; para-xylene
Other Properties
Soluble in ether and ethanol. Insoluble in water.
| Composition | C6H4(CH3)2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 1330-20-7 |
| Melting Point | (-25) - 13.2 |
| Density | 0.86 - 0.88 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt.=106.16 |
| Refractive Index | 1.493-1.494 |
| Boiling Point | 137 - 140 |
Hazards and Safety
Flammable, flash point 27C (81F). May be absorbed through the skin, can cause defatting and irritation. Inhalation of large amounts may be fatal (glue sniffer's syndrome).
Mallinckrodt Baker: MSDS
Comparisons
Authority
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 801
- Reed Kay, The Painter's Guide To Studio Methods and Materials, Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1983
- Marjorie Shelley, The Care and Handling of Art Objects, The Metropolitan Museum, New York, 1987
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Website address 1 Comment: www.hants.org.uk/museums/ofr/cmeth_t.html
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: ref. index=1.493 (p-xylene); 1.494 (m-xylene)