Berberis dye (berberis tibetasia) LC
thumb| from Denver Botanic Gardens
Description
Historical importance
Summary of results
Analytical instrumentation and procedures
HPLC-DAD-MS analysis was performed with an Agilent 1100 liquid chromatography system consisting of an automatic injector, a gradient pump, a HP series 1100 DAD, and an Agilent series 1100 VL on-line atmospheric pressure ionization electrospray ionization mass spectrometer. Separations were done on a Vydac 214TP52 analytical column (2.1 mm diameterX250 mm; 5-ím particle size). The column was eluted at a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min with a tertiary gradient of water (A),acetonitrile (B), and 1% (v/v) aqueous formic acid (C) with the following elution program: 0 min, 90% A, 5% B, 5% C; 0-55 min, a linear gradient to 35% A, 60% B, 5% C; 55-60 min, a linear gradient elution to 15% A, 80% B, 5% C; 60-62 min, isocratic elution at 15% A, 80% B, 5% C; 62-70 min gradient elution to 90% A, 5% B, 5% C; and reequilibration with the latter solvent for 15 min. The mass spectrometer was run both in the negative and positive ion mode.
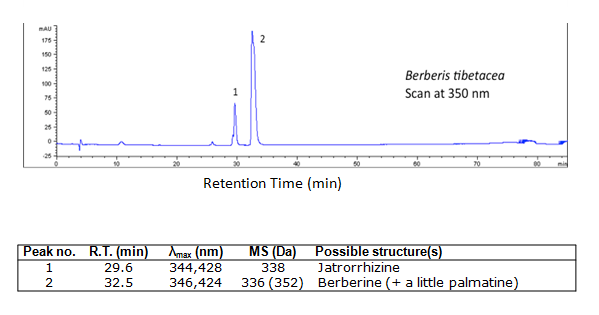
Chromatograms
berberis tibetasia dyed silk sample (direct dye without mordant) was extracted and the extract was injected in HPLC-DAD-MS for analysis.
HPLC-DAD profile and compounds identified
sample information
Identified compounds
| Compound | RT (min.) | MW | UV/vis | Other | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| palmatine | 32.5 | 351 | 348,428 | minor component | |
| jatrorrhizine | 29.6 | 337 | 348,428 | ||
| berberine | 32.5 | 335 | 348,428 | major component |
References
[1] [2] [3]