Barite
Description
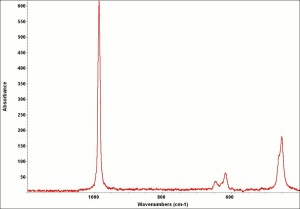
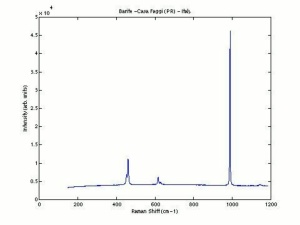
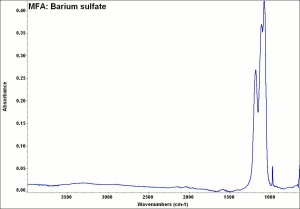
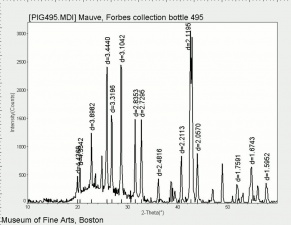
A heavy, white mineral composed of Barium sulfate. Barite occurs worldwide including Germany (North Rhine-Westphalia), France, Spain (Castile, Andalusia), England, Canada (Ontario, Nova Scotia, British Columbia), and the U.S.(New York, Connecticut, Pennsylvania, Virginia, Michigan, Missouri, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Utah, Colorado, South Dakota, Georgia, Tennessee, and California). The transparent to translucent stone can produce a sulfur-like odor when two pieces are rubbed together. Barite is ground to produce the natural form of barium sulfate white pigment called barium white that is often used as an extender.
Synonyms and Related Terms
barium sulfate; baryte; barium white; Pigment White 22 (natural); barus (Gr.); Baryt (Deut., Pol., Sven.); barytine, barite (Fr., Port.); baritina (Esp.); barita (Esp.); Schwerspat (Deut.); bariet (Ned.); heavy spar; baryta; Bologna stone; desert rose (red color, flower-like formation)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Orthorhombic crystal system with tabular, lamellar, or fibrous crystals.
- Perfect cleavage in one direction, good in a second direction.
- Fracture = uneven.
- Luster = vitreous;
- Streak = white;
- Low birefringence.
- Under cross polars, rotating the stage may cause the particles to twinkle.
| Composition | BaSO4 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 3.0 - 3.5 |
| Density | 4.3-4.6 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.636; 1.637; 1.648 |
Comparisons
Characteristics of Common White Pigments
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Barite
- Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, Pigment Compendium, Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004 Comment: Refractive index: alpha=1.634-1.637, beta=1.636-1.638, 1.646-1.648
Dispersion=0.010
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: Barite. Retrieved May 24, 2003
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 83
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia,: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barite (Accessed Oct. 18, 2005)
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998