Viridian
Description
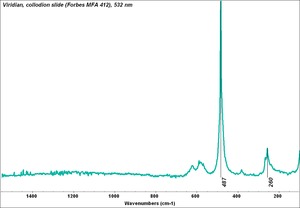
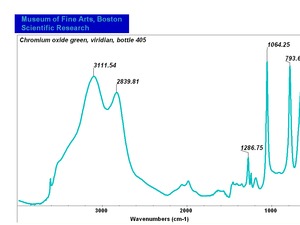
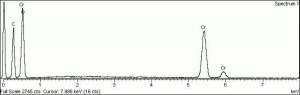
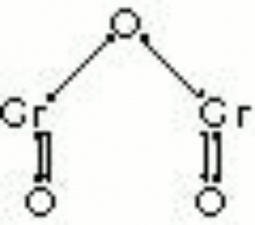
A permanent green pigment composed of hydrated chromium oxide. Viridian is a synthetic pigment with characteristic deep green, transparent particles which are unaffected by light and chemicals. The process for making the hydrated form of chromium oxide was discovered in 1838 by Pannetier in Paris. A less expensive method for manufacturing viridian was patented by Guignet in 1859. Viridian, though not extremely popular because of its high price, was used as a pigment in all types of binding media. The stable pigment is also used as a colorant in concrete mixtures, rubber, inks, and automotive paints.
Synonyms and Related Terms
chromium oxide hydrate; Pigment Green 18; CI 77289; transparent chrome oxide; vert émeraude (Fr.); Chromoxidhydratgrün (Deut.); Veridian (Deut); viridiana (Esp.); verde smeraldo (It.); viridiaan (Ned.); viridian (Port.); chromium oxide green transparent; chromium oxide dihydrate; French Veronese green; Pannetier's green; Mittlers' green; Guignet's green; Casali's green
Risks
- Gamblin Colors: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Resistant to acids and alkalis.
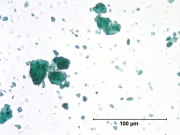
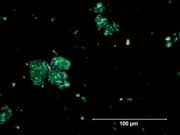
- Particle size irregular (0.07 - 20 micrometers).
- Irregular undulose extinction in polarized light.
- Bright green birefringent particles.
| Composition | Cr2O3.2H2O |
|---|---|
| CAS | 1308-38-9 |
| Melting Point | 2435 C |
| Density | 3.32 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.62; 2.12 |
| Boiling Point | 4000 C |
Resources and Citations
- R. Newman, "Chromium Oxide Greens", Artists Pigments, Volume 3, E. West FitzHugh (ed.), Oxford University Press: Oxford, 1997.
- The Dictionary of Art, Grove's Dictionaries Inc., New York, 1996 Comment: "Pigments"
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: p. 173
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Pigments Through the Ages - http://webexhibits.org/pigments/indiv/technical/viridian.html - refractive index: alpha and beta = 1.62; gamma = 2.12
- Thomas B. Brill, Light Its Interaction with Art and Antiquities, Plenum Press, New York City, 1980
- R.D. Harley, Artists' Pigments c. 1600-1835, Butterworth Scientific, London, 1982
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Viridian (Accessed Sept. 20, 2005)