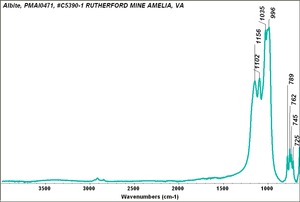
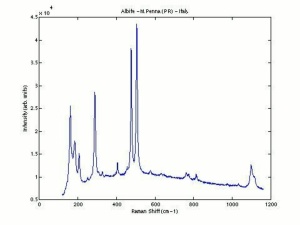
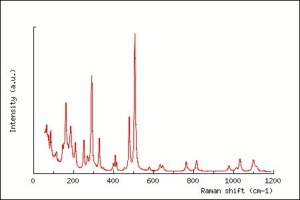
Albite
Description
A sodium plagioclase Feldspar mineral composed of sodium aluminum silicate. Albite is found throughout the world, with major locations in the Alps, Urals, Harz Mountains, France, Norway, and the U.S. (Maine, Virginia, Colorado). The mineral is translucent to opaque with a pearly luster. Although usually white, the brittle, glassy crystals that may be colorless, yellow, pink, green, or black. Albite is used in ceramics and in the manufacture of artificial teeth. It can cause unwanted bubbles in glazes at temperatures above 1200 C (Fournier 1996).
Synonyms and Related Terms
albus (Lat.); albita (Esp.); albite (Fr.; Port.); Albit (Deut.); albiet (Ned.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
Crystalline system = triclinic with tabular crystals, twinning is common.
Cleavage occurs at 86o24' angles
| Composition | Na[AlSi3O8] |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 6.0 |
| Density | 2.62 g/ml |
Resources and Citations
- Robert Fournier, Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery, Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992.
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: albite" [Accessed March 4, 2002].
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Albite (Accessed Mar. 15, 2006)
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=2.62-2.65