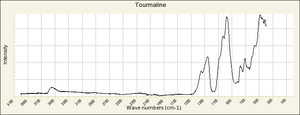
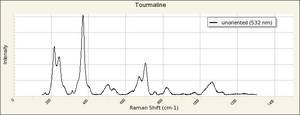
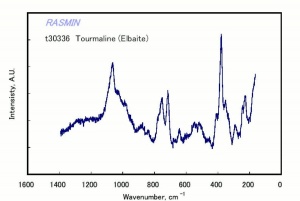
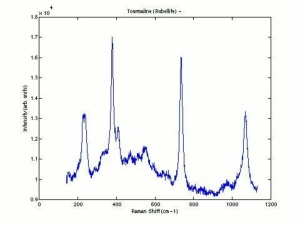
Tourmaline
Description
A semiprecious Gemstone composed of an aluminum borosilicate mineral. Tourmaline occurs in pegmatite deposits, such as found in the Ural Mountains, Bohemia, Germany (Saxony), India, the island of Elba, Norway, England, Greenland, Brazil, Madagascar, and the U.S. (New England, New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, California). Tourmalines can be opaque or transparent and range in color from black, dark blue (indicolite), light blue (Brazilian sapphire), brown (dravite), green (Brazilian emerald), red (rubellite) and, though rare, colorless (achroite). Opaque black tourmalines, called schorl, are the most common. Tourmalines form Static electricity when they are rubbed or heated. This property makes them useful in pressure gauges, oscillator plates, and other electrical equipment.
Synonyms and Related Terms
schorl (opaque black); tourmalin; turmaline; elbaite; indicolite (blue); rubellite (pink or red); dravite (brown); achroite (colorless); Brazilian sapphire (light blue); Brazilian emerald (green); Turmalin (Deut, Pol.); turmalina (Esp., Port.); tourmaline (Fr.); toermalijn (Ned.)
Risks
- Tourmaline is piezoelectric (develops a charge when heated) and may attract dust when displayed under a hot light.
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Hexagonal system with small, often rounded, hexagonal crystalline prisms, plates or wedges
- Fracture = conchoidal or uneven
- Luster = vitreous to resinous
- Streak = white
- Pleochroism = dichroic: medium to strong; usually two tones of gem color
- Fluorescence = variable; some pink stones may show weak red in LW and SW
| Composition | (Na,Ca)(Al,Fe)B3Al3(AlSi2O9)(O,OH,F)4 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 7.0 - 7.5 |
| Density | 2.9-3.2 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.63; 1.66 |
| Birefringence | 0.018 - 0.020 |
Comparisons
Properties of Common Gemstones
Natural and Simulated Diamonds
Resources and Citations
- Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016.
- Jack Odgen, Jewellery of the Ancient World, Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982
- R.F.Symmes, T.T.Harding, Paul Taylor, Rocks, Fossils and Gems, DK Publishing, Inc., New York City, 1997
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "tourmaline" [Accessed December 4, 2001]. (tech info)..
- Website: http://www.geo.utexas.edu/courses/347k/redesign/gem_notes/Tourmaline/tourm_triple_page.htm
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tourmaline (Accessed Sept. 17, 2005 and Dec 2022)
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 435
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=3.0-3.2