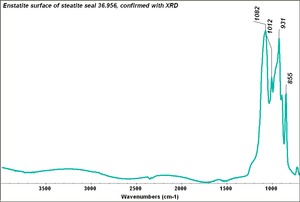
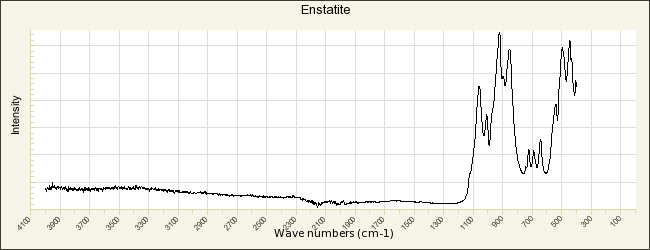
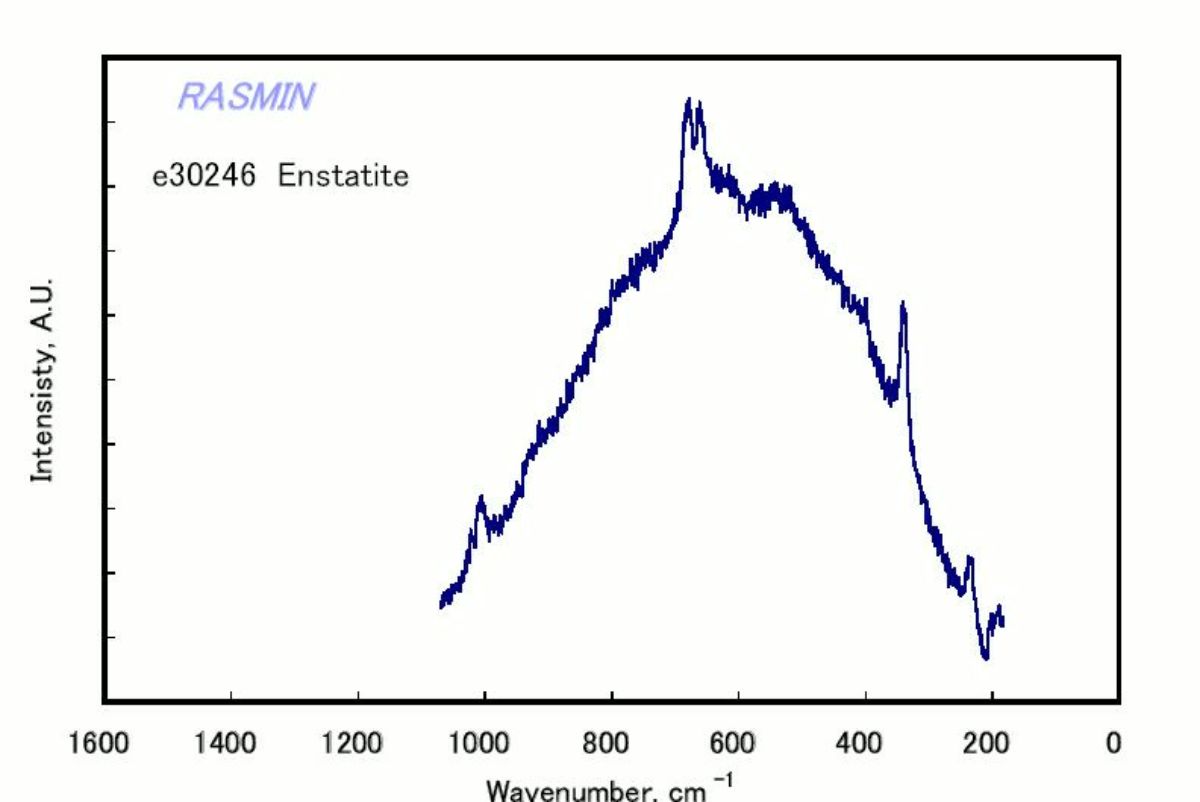
Enstatite
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Description
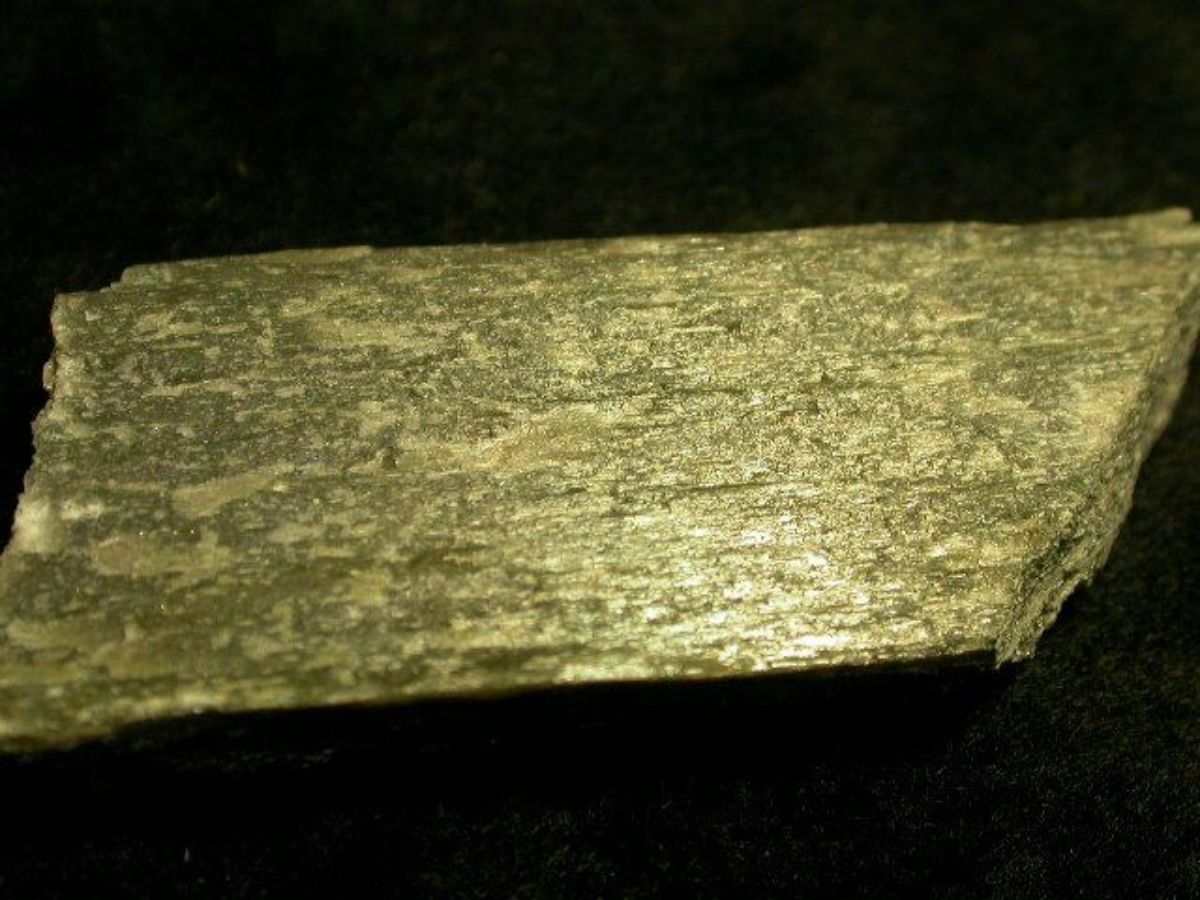
A pyroxene mineral composed of magnesium silicate. Enstatite was first described by G.A. Kenngott in 1855. It occurs naturally in metamorphic rocks and meterorites. The mineral is usually a gray, pale green, or brown in color although a gemstone quality emerald green variety occurs rarely. Weathered enstatite can have a metallic luster and is called bronzite. Enstatite can alter to form steatite. Steatite may also be heated to form enstatite.
Synonyms and Related Terms
bronzite; Enstatit (Deut.); enstatiet (Ned.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Orthorhombic crystal system with prismatic crystals commonly lamellar, fibrous or massive
- Cleavage = distinct in two directions
- Fracture = uneven
- Luster = vitreous to pearly
- Streak = gray
- Fluorescence = inert
- Pleochroism = weak to strong; pink to green; green to yellowish green; or brown to yellow
| Composition | MgSiO3 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 5 - 6 |
| Density | 3.21-3.96 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.650-1.679 |
| Birefringence | 0.008 - 0.11 |