Difference between revisions of "Acetanilide"
(username removed) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
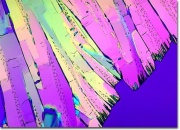
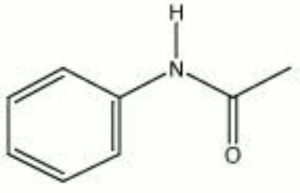
| − | A white, odorless powder that has a burning taste. Acetanilide is produced from aniline using [ | + | A white, odorless powder that has a burning taste. Acetanilide is produced from aniline using [[acetic%20acid|acetic acid]]. The shiny, leaflet crystals are stable in air. Acetanilide was used in the 19th century to treat fever and headaches but was discontinued because of toxic side effects. It is still used in the manufacture of medicines and dyes, as an accelerator for rubber [[vulcanization|vulcanization]], as a stabilizer for [[cellulose%20ester|cellulose ester]] dopes and lacquers, and as a synthetic [[camphor|camphor]]. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
Revision as of 13:43, 6 January 2014
Description
A white, odorless powder that has a burning taste. Acetanilide is produced from aniline using Acetic acid. The shiny, leaflet crystals are stable in air. Acetanilide was used in the 19th century to treat fever and headaches but was discontinued because of toxic side effects. It is still used in the manufacture of medicines and dyes, as an accelerator for rubber Vulcanization, as a stabilizer for Cellulose ester dopes and lacquers, and as a synthetic Camphor.
Synonyms and Related Terms
n-phenylacetamide; antifebrin; acetylaniline; acetylaminobenzene; acetic acid anilide; acetanil; n-acetylaniline; n-phenyl acetamide
Other Properties
Soluble in hot water, ethanol, ether, chloroform, acetone, glycerol and benzene.
| Composition | C8H9NO |
|---|---|
| CAS | 103-84-4 |
| Melting Point | 114-116 |
| Density | 1.2105 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt.=135.17 |
| Boiling Point | 303.8 |
Hazards and Safety
Highly toxic by ingestion. Causes cyanosis. Skin contact and inhalation cause irritation.
Mallinckrodt Baker: MSDS
Authority
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acetanilide (Accessed Oct. 18, 2005)
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998