Difference between revisions of "Category:Dayflower/Safflower: Ukiyo-e colorant"
| (16 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:SC214686.jpg|right|300px|link=Utamaro I, Courtesan Asajiu of the Daimonjiya and Nanatsu-ume Sake by Momenya, from the series Aristocrats of Sake Compared to Courtesans of Six Selected Houses, 11.14267|Courtesan Asajiu of the Daimonjiya and Nanatsu-ume Sake by Momenya by Kitagawa Utamaro I]] |
| − | <font size="3">'''[[:Category:Dayflower: Ukiyo-e colorant|Dayflower]] + [[:Category:Safflower: Ukiyo-e colorant|Safflower]]'''</font>: Purple is achieved by mixing | + | <font size="3">'''[[:Category:Dayflower: Ukiyo-e colorant|Dayflower]] + [[:Category:Safflower: Ukiyo-e colorant|Safflower]]'''</font>: Purple is achieved by overprinting or mixing a blue and a red colorant. The dominant purple used throughout the Edo period (1603–1868) is composed of dayflower and safflower. Initially, dayflower was printed over safflower as seen on early two to three color prints; by the 1770s onward, these colors were generally found mixed. By varying the proportions of dayflower to safflower, an array of cool to warm purples were achieved. Even after the introduction of [[:Category:Prussian Blue: Ukiyo-e colorant|Prussian blue]] in the 1820s, dayflower and safflower continued to be the preferred mixture. |
| + | On prints, this purple can appear brown to tan due to fading and/or shifting of dayflower and safflower. Damage from contact with moisture is frequently encountered because of the highly soluble nature of dayflower. When the print is exposed to water, the dayflower can disperse to reveal the safflower whether or not the purple was produced by overprinting or mixing. Also, the appearance of purple can be found altered from contact with moisture introduced during lining. The water content of the adhesive used to line a print can draw the dayflower into the lining paper, which effectively causes it to move from the print's surface towards the back and into the lining paper. | ||
'''For more information see:''' [[:Category:Dayflower: Ukiyo-e colorant|Dayflower]], [[:Category:Safflower: Ukiyo-e colorant|Safflower]] | '''For more information see:''' [[:Category:Dayflower: Ukiyo-e colorant|Dayflower]], [[:Category:Safflower: Ukiyo-e colorant|Safflower]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | == Examples of Dayflower+Safflower in Ukiyo-e Prints == | + | == Examples of Dayflower + Safflower in Ukiyo-e Prints == |
{|class="wikitable" style="display: inline-table;font-size:90%;text-align:center;width:15%" | {|class="wikitable" style="display: inline-table;font-size:90%;text-align:center;width:15%" | ||
| Line 42: | Line 44: | ||
== Analysis == | == Analysis == | ||
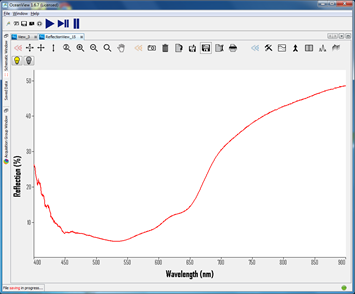
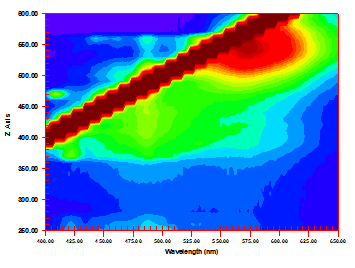
| − | Excitation Emission Matrix (EEM) spectroscopy | + | Fiber optic reflectance spectroscopy (FORS) and Excitation Emission Matrix (EEM) spectroscopy is used to identify dayflower + safflower. For more information, please see the individual colorant pages, [[:Category:Dayflower: Ukiyo-e colorant|dayflower]] and [[:Category:Safflower: Ukiyo-e colorant|safflower]]. |
<gallery mode="packed" heights="200px" style="text-align: left"> | <gallery mode="packed" heights="200px" style="text-align: left"> | ||
| − | + | FORS purple lining.png|<center>FORS of Dayflower + Safflower</center> | |
| − | + | EEM purple lining.png|<center>EEM of Dayflower + Safflower</center> | |
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Images of Dayflower + Safflower== | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
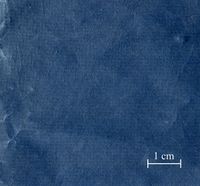
| + | File:Printed purple-cropped.jpg|Printed dayflower + safflower (overprinted) | ||
| + | File:Printed purple2-cropped.jpg|Printed dayflower + safflower (mixed) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==List of Prints == | ==List of Prints == | ||
| − | + | Below is a list of prints where dayflower + safflower was detected. | |
Latest revision as of 21:57, 8 April 2024
Dayflower + Safflower: Purple is achieved by overprinting or mixing a blue and a red colorant. The dominant purple used throughout the Edo period (1603–1868) is composed of dayflower and safflower. Initially, dayflower was printed over safflower as seen on early two to three color prints; by the 1770s onward, these colors were generally found mixed. By varying the proportions of dayflower to safflower, an array of cool to warm purples were achieved. Even after the introduction of Prussian blue in the 1820s, dayflower and safflower continued to be the preferred mixture.
On prints, this purple can appear brown to tan due to fading and/or shifting of dayflower and safflower. Damage from contact with moisture is frequently encountered because of the highly soluble nature of dayflower. When the print is exposed to water, the dayflower can disperse to reveal the safflower whether or not the purple was produced by overprinting or mixing. Also, the appearance of purple can be found altered from contact with moisture introduced during lining. The water content of the adhesive used to line a print can draw the dayflower into the lining paper, which effectively causes it to move from the print's surface towards the back and into the lining paper.
For more information see: Dayflower, Safflower
Examples of Dayflower + Safflower in Ukiyo-e Prints
|

|

|

|

|
Analysis
Fiber optic reflectance spectroscopy (FORS) and Excitation Emission Matrix (EEM) spectroscopy is used to identify dayflower + safflower. For more information, please see the individual colorant pages, dayflower and safflower.
Images of Dayflower + Safflower
List of Prints
Below is a list of prints where dayflower + safflower was detected.
Pages in category "Dayflower/Safflower: Ukiyo-e colorant"
The following 53 pages are in this category, out of 53 total.
E
- Eisen, Early Winter: The Day of the Boar in the Tenth Month, from the series Customs of the Four Seasons and Children at Play, 11.25587
- Eisen, Fujieda: Kichô of the Owariya, from the series A Tôkaidô Board Game of Courtesans: Fifty-three Pairings in the Yoshiwara, 11.17946
- Eisen, Kawasaki, No. 3 from an untitled series of the Fifty-three Stations of the Tôkaidô Road, 11.25617
- Eisen, Minazuru-hime as Ono no Komachi and Benkei as Kisen Hôshi, from the series Characters from the Life of Ushiwaka as the Six Poetic Immortals, 11.25669
- Eishi, Shizuka of the Shizutamaya, from the series Beauties of the Yoshiwara as Six Floral Immortals, 21.4917
- Eishi, Shizuka of the Shizutamaya, from the series Beauties of the Yoshiwara as Six Floral Immortals, 53.21
H
- Harunobu, A Young Woman in a Summer Shower, 11.19430
- Harunobu, Courtesan and Kamuro Looking at the Face of a Komusô Reflected in a Mirror, 45.833
- Harunobu, Courtesan Reading a Letter by Moonlight Reflected on Snow; Parody of Son Kang, 11.19438
- Harunobu, Courtesan Watching Two Kamuro Make a Snow Dog, 21.4463
- Harunobu, Ebisu and Ofuji, from the series The Seven Gods of Good Fortune in the Modern World, 34.343
- Harunobu, Nishikigi of the Kanaya Lighting Incense beside a Mosquito Net, 11.16479
- Harunobu, Osen of the Kagiya and a Young Man with a Cat, 11.19496
- Harunobu, Parody of Saigyô Hôshi: Courtesan Looking at a Screen Painting of Mount Fuji, 11.19431
- Harunobu, Poem by Saigyô Hôshi, from an untitled series of Three Evening Poems, 34.348
- Harunobu, The Eleventh Month, from an untitled series of Twelve Months, 11.20120
- Harunobu, The Sake Cup, sheet 4 of the series Marriage in Brocade Prints, the Carriage of the Virtuous Woman, known as the Marriage series, 11.19475
- Harunobu, The Tenth Month, from an untitled series of Twelve Months, 11.20124
- Hiroshige I, Naitô Shinjuku, Yotsuya, from the series One Hundred Famous Views of Edo, 11.35823
- Hiroshige I/Hiroshige II, Ueno Yamashita, from the series One Hundred Famous Views of Edo, 11.35842
- Hokkei, Goat Standing by a Plum Tree, 21.9277
K
- Kiyomitsu I, Yoritomo's Hunt at the Foot of Mount Fuji, 11.19694
- Kiyonaga, A Matchmaking Meeting at a Teahouse by a Shrine, 21.5574
- Kiyonaga, Actors Matsumoto Kôshirô IV as Ukita Sakingo and Sawamura Sôjûrô III as the Ghost of Takao, with chanters Tomimoto Itsukidayû and Tomimoto Awatayû, and accompanist Sasaki Ichishirô, 11.13921
- Kiyonaga, Actors Matsumoto Kôshirô IV as Ukita Sakingo and Sawamura Sôjûrô III as the Ghost of Takao, with chanters Tomimoto Itsukidayû and Tomimoto Awatayû, and accompanist Sasaki Ichishirô, 21.5476
- Kiyonaga, The Brine Maidens, from the series Current Manners in Eastern Brocade, 11.13880
- Kiyonaga, The Brine Maidens, from the series Current Manners in Eastern Brocade, 21.5610
- Kiyonaga, Women Visiting Enoshima, 11.21277
- Kokan, Couple Cooling Off on a Garden Bench, 11.19524
- Koryusai, Descending Geese at Mimeguri, from the series Fashionable Eight Views of Edo, 11.14627
- Koryusai, Twilight Snow of the Bride, from the series Eight Views of Fashionable Human Relations, 11.19541
- Kunisada, Actor Sawamura Tanosuke II, from the series Actor Rebuses, 11.42324
- Kunisada, Poem by Ariwara no Narihira Ason: (Actor Ichikawa Danjûrô VIII as) Seigen, from the series Comparisons for Thirty-six Selected Poems, 11.42663
- Kunisada, Young Woman Pointing and Giggling, from the series Types of the Floating World Seen through a Physiognomist's Glass, 34.471
- Kuniyoshi, (Actor Ichikawa Ebizô V as) Inuyama Dôsetsu, from the series The Lives of Eight Brave and Loyal Dog Heroes, 11.28841
- Kuniyoshi, Actor Ichikawa Kodanji IV as the Ghost of Asakura Tôgo, 11.30460
- Kuniyoshi, Drying Board Suggesting Hiyodorigoe, from the series Women in Benkei-checked Fabrics, 11.36363
- Kuniyoshi, Hosokute: Horikoshi Dairyô, from the series Sixty-nine Stations of the Kisokaidô Road, 11.28766
- Kuniyoshi, Takeout Sushi Suggesting Ataka, from the series Women in Benkei-checked Fabrics, 11.36360
- Kuniyoshi, Tsumagome: Abe no Yasuna and the Fox Kuzunoha, from the series Sixty-nine Stations of the Kisokaidô Road, 11.41803
S
- Sharaku, Actor Osagawa Tsuneyo II as Ippei's Older Sister Osan, 11.14673
- Sharaku, Actor Osagawa Tsuneyo II as Ippei's Older Sister Osan, 11.14674
- Sharaku, Actor Osagawa Tsuneyo II as Ippei's Older Sister Osan, 21.7244
- Shigenobu I, Puppy Playing with a Ball, 21.9257
- Shigenobu I, Urashima Tarô, from the series A Set of Five Examples of Longevity, 21.9254
- Shinsai, Chapters 25–27, from the series The Tale of Genji, 21.9264
- Shunkō, Actors Ichikawa Danjûrô V as Fukurokuju, Iwai Hanshirô IV as Ryûyô Dôji, and Sawamura Sôjûrô III as Shin'yô Dôji, 11.14971
- Shunman, Mandarin Ducks and Iris, from the series Series of Seven Bird-and-Flower Prints for the Fuyô Circle of Kanuma in Shimotsuke Province, 21.9226
- Shunshō, No. 3, Comparative Poems, from the series Six Types of Waka Poetry as Described in the Preface of the Kokinshû, 11.19295
- Shunshō, No. 6, Cui Zongzhi (Saisôshi), from the series Eight Immortals of The Wine Cup, 11.14847
U
- Utamaro I, Courtesan Asajiu of the Daimonjiya and Nanatsu-ume Sake by Momenya, from the series Aristocrats of Sake Compared to Courtesans of Six Selected Houses, 11.14267
- Utamaro I, Kitchen Scene, 34.269a-b
- Utamaro I, The Heron Maiden from series An Array of Dancing Girls of the Present Day, 11.14364