Difference between revisions of "Category:Sappanwood: Ukiyo-e colorant"
(Created page with "== Description == Sappanwood (suo): A natural red dye produced from the hot water extraction of any of several tropical trees of the senna genus, ''Caesalpinia'', such as ''C...") |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
File:brazilwood raw.jpg|Cut pieces of brazilwood (''Caesalpinia brasiliensis'') | File:brazilwood raw.jpg|Cut pieces of brazilwood (''Caesalpinia brasiliensis'') | ||
File:Red bud_suo.jpg|Red bud | File:Red bud_suo.jpg|Red bud | ||
| − | File: | + | File:12 Sappanwood.jpg|Sappanwood, poowdered |
File:06_Brazilwood comp.jpg|Dye mixtures from brazilwood juice | File:06_Brazilwood comp.jpg|Dye mixtures from brazilwood juice | ||
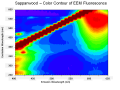
| + | Sappanwood color.PNG|EEM Color | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Examples == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Ukiyo-e Colorants]] | ||
Revision as of 10:13, 29 April 2020
Description
Sappanwood (suo): A natural red dye produced from the hot water extraction of any of several tropical trees of the senna genus, Caesalpinia, such as C. brasiliensis (from Brazil), C. crista (from Pernambuco), C. echinata (peachwood from Nicaraugua), or C. sappan (sappanwood from East Indies and Asia). Brazilwood was used to dye textiles as early as the 12th century in Europe. Its principal colorant is Brasilin, a hydroxyanthraquinone, that gives a deep red to brownish color when it is oxidized to form brasilein. Brazilwood produces purple shades with a chrome mordant and crimson shades with alum. When mordanted on chalk, brazilwood produces lakes ranging in colors from lavender to cherry to deep red. It was a cheaper red lake pigment than carmine. Brazilwood dye has been used for textile dyes, inks, paints, varnish tints, and wood stains. The color is not lightfast and fades when heated.
Examples
Pages in category "Sappanwood: Ukiyo-e colorant"
The following 37 pages are in this category, out of 37 total.
B
E
- Eisen, Kawasaki, No. 3 from an untitled series of the Fifty-three Stations of the Tôkaidô Road, 11.25617
- Eisen, Minazuru-hime as Ono no Komachi and Benkei as Kisen Hôshi, from the series Characters from the Life of Ushiwaka as the Six Poetic Immortals, 11.25669
- Eisen, The Song Evening Mist at Asama Peak, on Scrap-paper Fabric with an Itchû-bushi Libretto, from the series A Modern Pine Needle Collection, 11.17878
H
- Harunobu, Courtesan Watching Two Kamuro Make a Snow Dog, 21.4463
- Harunobu, Osen of the Kagiya and a Young Man with a Cat, 11.19496
- Harunobu, Parody of Saigyô Hôshi: Courtesan Looking at a Screen Painting of Mount Fuji, 11.19431
- Harunobu, The Tenth Month, from an untitled series of Twelve Months, 11.20124
- Harunobu, Young Woman Tuning a Shamisen, 06.479
- Hiroshige I, Naitô Shinjuku, Yotsuya, from the series One Hundred Famous Views of Edo, 11.35823
- Hiroshige I, Pine of Success and Oumayagashi, Asakusa River, from the series One Hundred Famous Views of Edo, 11.17029
- Hokkei, Goat Standing by a Plum Tree, 21.9277
- Hokkei, Ômori, from the series Souvenirs of Enoshima, a Set of Sixteen, 11.19845
K
- Kiyomasu II, Actors Ôtani Hiroji II as Washi no Chôkichi and Arashi Tominosuke as Tarui Osen, 21.5458
- Kokan, Couple Cooling Off on a Garden Bench, 11.19524
- Komatsuken, Courtesan Parading with Two Kamuro, 11.19711
- Komatsuken, Young Man as the Bodhisattva Monju, 11.30137
- Komatsuken, Young Woman as the Bodhisattva Fugen, 11.30136
- Koryusai, Descending Geese at Mimeguri, from the series Fashionable Eight Views of Edo, 11.14627
- Kunisada, Poem by Ariwara no Narihira Ason: (Actor Ichikawa Danjûrô VIII as) Seigen, from the series Comparisons for Thirty-six Selected Poems, 11.42663
- Kunisada, Young Woman Pointing and Giggling, from the series Types of the Floating World Seen through a Physiognomist's Glass, 34.471
- Kuniyoshi, Actor Ichikawa Kodanji IV as the Ghost of Asakura Tôgo, 11.30460
- Kuniyoshi, Hosokute: Horikoshi Dairyô, from the series Sixty-nine Stations of the Kisokaidô Road, 11.28766
- Kuniyoshi, Takeout Sushi Suggesting Ataka, from the series Women in Benkei-checked Fabrics, 11.36360
- Kuniyoshi, Tsumagome: Abe no Yasuna and the Fox Kuzunoha, from the series Sixty-nine Stations of the Kisokaidô Road, 11.41803
S
- Sharaku, Actor Osagawa Tsuneyo II as Ippei's Older Sister Osan, 11.14673
- Sharaku, Actor Osagawa Tsuneyo II as Ippei's Older Sister Osan, 11.14674
- Sharaku, Actor Osagawa Tsuneyo II as Ippei's Older Sister Osan, 21.7244
- Shigenobu I, Puppy Playing with a Ball, 21.9257
- Shinsai, Chapters 22–24, from the series The Tale of Genji, 11.20034
- Shinsai, Chapters 25–27, from the series The Tale of Genji, 21.9264
- Shunkō, Actors Nakamura Nakazô I and Ôtani Hiroji III, 11.2014