Difference between revisions of "Chromatography"
(username removed) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
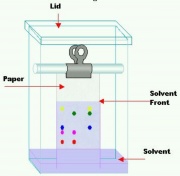
| − | A set of techniques used to separate mixtures of compounds. Chromatography was invented in 1906 by M. Tswett who used it to separate chlorophyll from ground plant material. Each method uses column or plate with a stationary phase (liquid or solid) and a mobile phase (gas or liquid). Separation occurs due to the selective absorption and desorption of compounds on the stationary phase as the mobile phase moves past. Compounds attracted to (or similar to) the stationary phase will be absorbed part of the time causing them to elute slowly while compounds that are not retained will be carried along by the mobile phase and elute quickly. See also [ | + | A set of techniques used to separate mixtures of compounds. Chromatography was invented in 1906 by M. Tswett who used it to separate chlorophyll from ground plant material. Each method uses column or plate with a stationary phase (liquid or solid) and a mobile phase (gas or liquid). Separation occurs due to the selective absorption and desorption of compounds on the stationary phase as the mobile phase moves past. Compounds attracted to (or similar to) the stationary phase will be absorbed part of the time causing them to elute slowly while compounds that are not retained will be carried along by the mobile phase and elute quickly. See also [[gas chromatography]], [[liquid chromatography]], [[size exclusion chromatography]], [[ion chromatography]], [[column chromatography]], [[paper chromatography]], and [[thin layer chromatography]]. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
Revision as of 09:41, 13 January 2014
Description
A set of techniques used to separate mixtures of compounds. Chromatography was invented in 1906 by M. Tswett who used it to separate chlorophyll from ground plant material. Each method uses column or plate with a stationary phase (liquid or solid) and a mobile phase (gas or liquid). Separation occurs due to the selective absorption and desorption of compounds on the stationary phase as the mobile phase moves past. Compounds attracted to (or similar to) the stationary phase will be absorbed part of the time causing them to elute slowly while compounds that are not retained will be carried along by the mobile phase and elute quickly. See also Gas chromatography, Liquid chromatography, Size exclusion chromatography, Ion chromatography, Column chromatography, Paper chromatography, and Thin layer chromatography.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Chromatographie (Deut.); chromatographie (Fr.);
Examples: gas chromatography; liquid chromatography; gel permeation chromatography; ion-exchange chromatography; column chromatography; paper chromatography; thin layer chromatography