Difference between revisions of "Excitation emission matrix (EEM)"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Excitation Emission Matrix Horiba.jpg|thumb|Exictation Emission Matrix plot from Horiba: [https://www.horiba.com/int/scientific/technologies/fluorescence-spectroscopy/what-is-an-excitation-emission-matrix-eem/ EEM]]] | [[File:Excitation Emission Matrix Horiba.jpg|thumb|Exictation Emission Matrix plot from Horiba: [https://www.horiba.com/int/scientific/technologies/fluorescence-spectroscopy/what-is-an-excitation-emission-matrix-eem/ EEM]]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
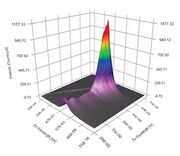
| − | The Excitation Emission Matrix (EEM) is a specific measurement that is becoming more widely used within the field of fluorescence spectroscopy. | + | The Excitation Emission Matrix (EEM) is a specific measurement that is becoming more widely used within the field of fluorescence spectroscopy. In a typical fluorescence (emission) measurement, the excitation wavelength is fixed and the detection wavelength varies, while in a fluorescence excitation measurement the detection wavelength is fixed and the excitation wavelength is varied across a region of interest. An emission map is measured by recording the emission spectra resulting from a range of excitation wavelengths and combining them all together. This compilation is a three dimensional scan that results can best be represented as a contour plot of excitation wavelength vs. emission wavelength vs. fluorescence intensity. |
| − | + | [[File: Madder color.PNG|thumb|EEM color contour map for madder on paper (MFA) | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | In a typical fluorescence (emission) measurement, the excitation wavelength is fixed and the detection wavelength varies, while in a fluorescence excitation measurement the detection wavelength is fixed and the excitation wavelength is varied across a region of interest. An emission map is measured by recording the emission spectra resulting from a range of excitation wavelengths and combining them all together. This is a three dimensional | ||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
Revision as of 14:48, 21 June 2023
Description
The Excitation Emission Matrix (EEM) is a specific measurement that is becoming more widely used within the field of fluorescence spectroscopy. In a typical fluorescence (emission) measurement, the excitation wavelength is fixed and the detection wavelength varies, while in a fluorescence excitation measurement the detection wavelength is fixed and the excitation wavelength is varied across a region of interest. An emission map is measured by recording the emission spectra resulting from a range of excitation wavelengths and combining them all together. This compilation is a three dimensional scan that results can best be represented as a contour plot of excitation wavelength vs. emission wavelength vs. fluorescence intensity. [[File: Madder color.PNG|thumb|EEM color contour map for madder on paper (MFA)
Synonyms and Related Terms
EEM; Excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy; Flourescence spectroscopy; fluorimetry; spectrofluorometry
Resources and Citations
- Wikipedia: Fluorescence spectroscopy
- Horiba: EEM