Difference between revisions of "Polystyrene"
(username removed) |
(username removed) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A thermoplastic polymer made from styrene. Although probably known earlier, polystyrene was described in 1839 by E. Simon of Germany, after he watched the clear [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=styrene styrene] liquid distilled from [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=storax storax] resin cool then harden to form a solid mass. Polystyrene was first commercially made in 1929 by I.G. Farben (Germany) for use in [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=styrene-butadiene | + | A thermoplastic polymer made from styrene. Although probably known earlier, polystyrene was described in 1839 by E. Simon of Germany, after he watched the clear [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=styrene styrene] liquid distilled from [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=storax storax] resin cool then harden to form a solid mass. Polystyrene was first commercially made in 1929 by I.G. Farben (Germany) for use in [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=styrene-butadiene%20rubber styrene butadiene] synthetic rubbers. Polystyrene is a hard, strong solid with good dimensional stability and impact resistance; it can be molded and fabricated. Polystyrene is often prepared as an expanded foam ([http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=Styrofoam%C2%AE Styrofoam®]) using blowing agents for use in temperature and sound insulation. It can be co-polymerized with many other polymers for increased flexibility, i.e. ABS rubbers are made from acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene. Polystyrene is used in insulation, toys, appliances, cabinets, containers, and furniture. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | PS; styrene polymer; | + | PS; styrene polymer; polystyrène (Fr.); poliestireno (Esp.); polistirene (It.); poliestireno (Port.); styrene resin |
| − | Examples: | + | Examples: Styrofoam® [Dow]; Luran; Styron; Lustrex; Fome-Cor®; Algil [Polymers, Inc.]; Permene [Modglin Co.]; Shalon [Polymers, Inc.]; Polyfil [Mack Molding]; Durastran |
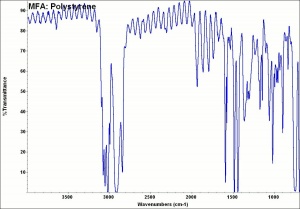
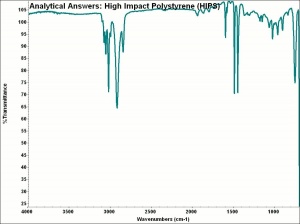
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|MFA- Polystyrene.jpg~FTIR|aaiHIPSpolystyrene.jpg~FTIR]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|MFA- Polystyrene.jpg~FTIR|aaiHIPSpolystyrene.jpg~FTIR]]] | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
| − | * | + | * R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: ref.index= 1.50-1.75 |
| − | * | + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: ref. index = 1.59 |
* ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | * ''Dictionary of Building Preservation'', Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996 | ||
| − | * | + | * Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', ''Engineered Plastics'', ASM International, 1988 |
| − | * | + | * Lynda A. Zycherman, J.Richard Schrock, ''A Guide to Museum Pest Control'', FAIC and Association of Systematics Collections, Washington DC, 1988 |
| − | * | + | * R.D. Harley, ''Artists' Pigments c. 1600-1835'', Butterworth Scientific, London, 1982 |
| − | * | + | * Pam Hatchfield, ''Pollutants in the Museum Environment'', Archetype Press, London, 2002 |
| − | * | + | * Thomas C. Jester (ed.), ''Twentieth-Century Building Materials'', McGraw-Hill Companies, Washington DC, 1995 |
| − | * | + | * M.Kaufman, ''The First Century of Plastics'', The Plastics and Rubber Institute, London, 1963 Comment: first developed commercially in 1930 |
| − | * | + | * F. Kidd, ''Brushmaking Materials'', Bristish Brush Manufacturers, London, 1957 |
| − | * | + | * Sharon Blank, An introduction to plastics and rubbers in collections, ''Studies in Conservation'', 35, 53-63, 1990 Comment: used in synthetic rubbers since 1927... it was first used as polystyrene in the mid 1930s |
* Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000 | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000 | ||
| − | * | + | * Website address 1 Comment: www.nswpmith.com.au/historyofplastics.html In Europe, I.G.Farbenindustrie: experiments 1924, production 1929 In US, Dow Chemical: experiments before 1930, production 1937 |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Revision as of 07:54, 24 July 2013
Description
A thermoplastic polymer made from styrene. Although probably known earlier, polystyrene was described in 1839 by E. Simon of Germany, after he watched the clear styrene liquid distilled from storax resin cool then harden to form a solid mass. Polystyrene was first commercially made in 1929 by I.G. Farben (Germany) for use in styrene butadiene synthetic rubbers. Polystyrene is a hard, strong solid with good dimensional stability and impact resistance; it can be molded and fabricated. Polystyrene is often prepared as an expanded foam (Styrofoam®) using blowing agents for use in temperature and sound insulation. It can be co-polymerized with many other polymers for increased flexibility, i.e. ABS rubbers are made from acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene. Polystyrene is used in insulation, toys, appliances, cabinets, containers, and furniture.
Synonyms and Related Terms
PS; styrene polymer; polystyrène (Fr.); poliestireno (Esp.); polistirene (It.); poliestireno (Port.); styrene resin
Examples: Styrofoam® [Dow]; Luran; Styron; Lustrex; Fome-Cor®; Algil [Polymers, Inc.]; Permene [Modglin Co.]; Shalon [Polymers, Inc.]; Polyfil [Mack Molding]; Durastran
Other Properties
Attacked by hydrocarbon solvents, oils, ketones, esters, inorganic acids.
Resistant to organic acids, alkalis, alcohols. Shrinks in boiling water.
Burns with luminous smoky flame giving faint odor of marigolds.
| Composition | [-C6H5CHCH2-]n |
|---|---|
| CAS | 9003-53-6 |
| Melting Point | softens about 150C |
| Density | 1.060 |
| Refractive Index | 1.59 |
Hazards and Safety
Combustible. Degrades in UV light.
Aldrich Chemical: MSDS
Comparisons
General Characteristics of Polymers
Physical Properties for Selected Thermoplastic Resins
Authority
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: ref.index= 1.50-1.75
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: ref. index = 1.59
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', Engineered Plastics, ASM International, 1988
- Lynda A. Zycherman, J.Richard Schrock, A Guide to Museum Pest Control, FAIC and Association of Systematics Collections, Washington DC, 1988
- R.D. Harley, Artists' Pigments c. 1600-1835, Butterworth Scientific, London, 1982
- Pam Hatchfield, Pollutants in the Museum Environment, Archetype Press, London, 2002
- Thomas C. Jester (ed.), Twentieth-Century Building Materials, McGraw-Hill Companies, Washington DC, 1995
- M.Kaufman, The First Century of Plastics, The Plastics and Rubber Institute, London, 1963 Comment: first developed commercially in 1930
- F. Kidd, Brushmaking Materials, Bristish Brush Manufacturers, London, 1957
- Sharon Blank, An introduction to plastics and rubbers in collections, Studies in Conservation, 35, 53-63, 1990 Comment: used in synthetic rubbers since 1927... it was first used as polystyrene in the mid 1930s
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000
- Website address 1 Comment: www.nswpmith.com.au/historyofplastics.html In Europe, I.G.Farbenindustrie: experiments 1924, production 1929 In US, Dow Chemical: experiments before 1930, production 1937