Difference between revisions of "Sycamore fig"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
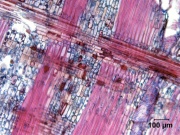
| − | [[File:97_Ficus_sycamorus_100X_Rad.jpg|thumb|Sycamore fig | + | [[File:97_Ficus_sycamorus_100X_Rad.jpg|thumb|Sycamore fig (''Ficus sycamorus'')<br> radial section at 100x]] |
| − | |||
| − | (''Ficus sycamorus'')]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
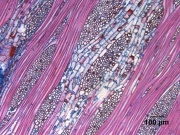
| + | [[File:97_Ficus_sycamorus_100X_Tan.jpg|thumb|Sycamore fig (''Ficus sycamorus'')<br> tangential section at 100x]] | ||
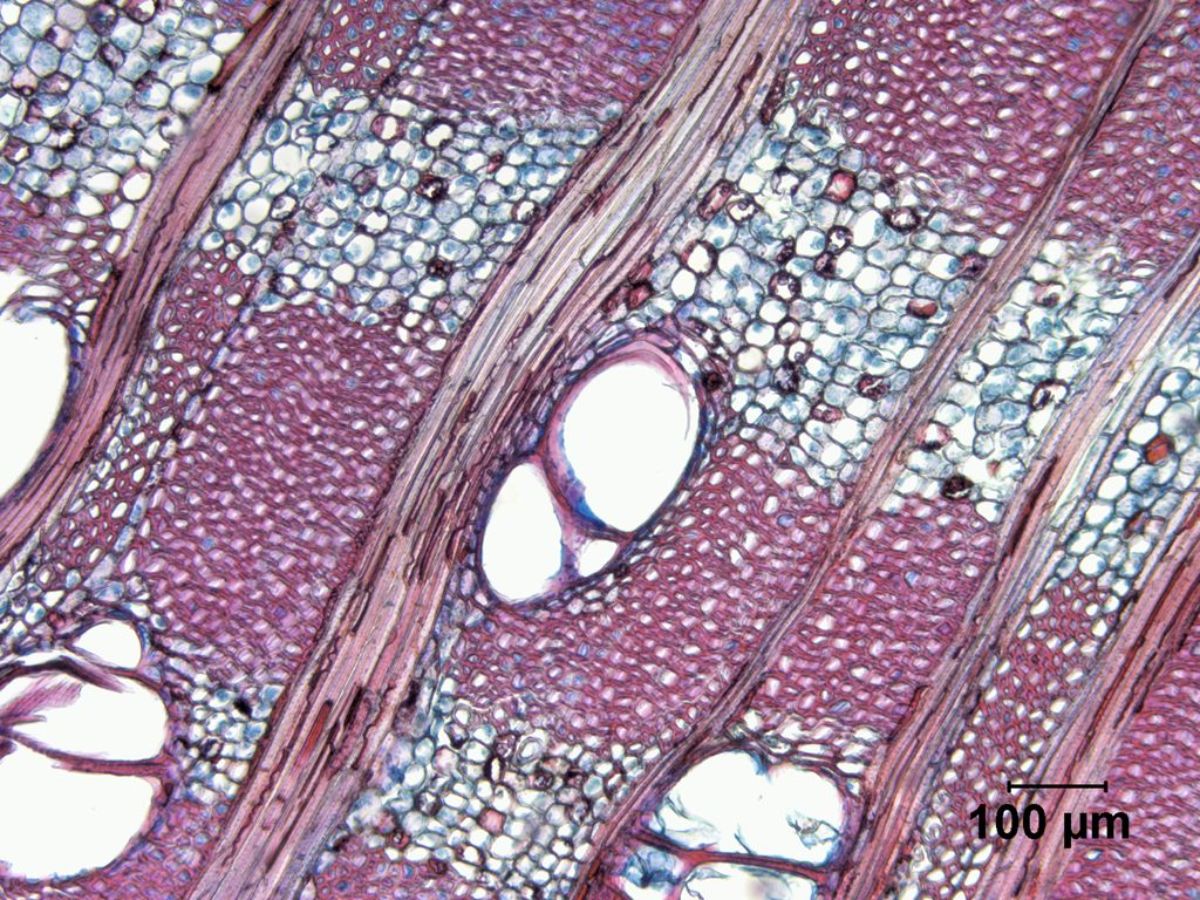
| + | [[File:97_Ficus_sycamorus_100X_Tran.jpg|Sycamore fig (''Ficus sycamorus'')<br> transverse section at 100x]] | ||
A tall, fig tree, ''Ficus sycamorus'', native to Africa, the Near East and southwest Asia. The sycamore fig produces a light, fibrous wood with a coarse texture. It was used in ancient Egypt for roof timbers, mummy cases, wagons, and statues (Gale et al 2000). | A tall, fig tree, ''Ficus sycamorus'', native to Africa, the Near East and southwest Asia. The sycamore fig produces a light, fibrous wood with a coarse texture. It was used in ancient Egypt for roof timbers, mummy cases, wagons, and statues (Gale et al 2000). | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | Ficus sycamorus; Egyptian fig tree; sycomore fig (sp) | + | ''Ficus sycamorus''; Egyptian fig tree; sycomore fig (sp) |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ==Resources and Citations== | ||
| − | + | * R.Gale, P.Gasson, N.Hepper, G.Killen, "Wood" in ''Ancient Egyptian Materials and Technology'', P.Nicholson, I.Shaw (eds.), Cambridge University Press, 2000, p. 334-371. | |
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 | ||
| Line 30: | Line 18: | ||
* Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | ||
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Sycamore." | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Sycamore." Accessed 21 May 2004. |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Revision as of 13:13, 7 June 2022
Description
A tall, fig tree, Ficus sycamorus, native to Africa, the Near East and southwest Asia. The sycamore fig produces a light, fibrous wood with a coarse texture. It was used in ancient Egypt for roof timbers, mummy cases, wagons, and statues (Gale et al 2000).
Synonyms and Related Terms
Ficus sycamorus; Egyptian fig tree; sycomore fig (sp)
Resources and Citations
- R.Gale, P.Gasson, N.Hepper, G.Killen, "Wood" in Ancient Egyptian Materials and Technology, P.Nicholson, I.Shaw (eds.), Cambridge University Press, 2000, p. 334-371.
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Sycamore." Accessed 21 May 2004.