Difference between revisions of "Kaolin"
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:Thomas Davies Pottery 2011.1807.jpg|thumb| | + | [[File:Thomas Davies Pottery 2011.1807.jpg|thumb|Face jug<br>MFA #: 2011.1807]] |
| + | [[File:B1216.jpg|thumb|Kaolin lion head from horse harness<br> MFA # 98.694]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
A type of [[primary clay] formed by the weathering of aluminum silicates, such as [[feldspar|feldspars]] and [[nepheline]]. When pure, kaolin is a soft, white, absorbent powder composed primarily of the mineral [[kaolinite]], a hydrated aluminum silicate. Impurities, such as iron oxide, silica, and other minerals, can produce yellow, red, blue, gray, or brownish color clays. Kaolin occurs at many locations around the world (France, England, Germany, China, United States, etc.). Kaolin is used to produce fine quality [[porcelain]] and china. It is also used as a base for lake colors and as a filler in paints, pastels, papers, rubbers, cements, and epoxies. Kaolin (as brick dust) has been used as an [[abrasive]] for polishing [[gold]] and other metals. It is also a useful [[absorbent]] for oils and greases and has been used commercially for cleaning fabrics, furs, and carpets. | A type of [[primary clay] formed by the weathering of aluminum silicates, such as [[feldspar|feldspars]] and [[nepheline]]. When pure, kaolin is a soft, white, absorbent powder composed primarily of the mineral [[kaolinite]], a hydrated aluminum silicate. Impurities, such as iron oxide, silica, and other minerals, can produce yellow, red, blue, gray, or brownish color clays. Kaolin occurs at many locations around the world (France, England, Germany, China, United States, etc.). Kaolin is used to produce fine quality [[porcelain]] and china. It is also used as a base for lake colors and as a filler in paints, pastels, papers, rubbers, cements, and epoxies. Kaolin (as brick dust) has been used as an [[abrasive]] for polishing [[gold]] and other metals. It is also a useful [[absorbent]] for oils and greases and has been used commercially for cleaning fabrics, furs, and carpets. | ||
| − | |||
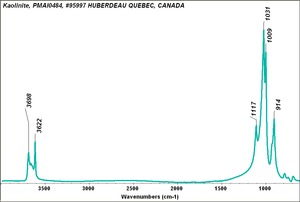
[[File:kaolinemr1.jpg|thumb|Kaolin]] | [[File:kaolinemr1.jpg|thumb|Kaolin]] | ||
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Kaolinite PMA.TIF~FTIR (MFA)]]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
kaolinite; China clay; Devonshire clay; Pigment White 19; CI 77005; Kaolinit (Deut.); Satinkreide (Deut.); caolín (Esp.); kaoliini (Fin.); kaolin (Fr.); blanc de Chine (Fr.); kaolinis (Gr.); caolino (It.); terra bianca (It.); bolo bianco (It.); creta Eretria (old Roman); bolus alba (old Roman); kaolien (Ned.); caulino (Port.); satinkrita (Sven.); dkar po (Tibetan); bolus alba; porcelain clay; white bole; argilla; paper clay; brick dust; fuller's earth; white bolus; white heart; pipe clay; pipeclay; | kaolinite; China clay; Devonshire clay; Pigment White 19; CI 77005; Kaolinit (Deut.); Satinkreide (Deut.); caolín (Esp.); kaoliini (Fin.); kaolin (Fr.); blanc de Chine (Fr.); kaolinis (Gr.); caolino (It.); terra bianca (It.); bolo bianco (It.); creta Eretria (old Roman); bolus alba (old Roman); kaolien (Ned.); caulino (Port.); satinkrita (Sven.); dkar po (Tibetan); bolus alba; porcelain clay; white bole; argilla; paper clay; brick dust; fuller's earth; white bolus; white heart; pipe clay; pipeclay; | ||
| + | ==Risks== | ||
| + | * Noncombustible | ||
| + | * ThermoFisher: [https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=AC211740010&productDescription=KAOLIN+1KG&vendorId=VN00032119&countryCode=US&language=en SDS] | ||
| + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
| − | = | + | * Composition = Al2Si2O5(OH4) |
| − | + | * Mohs Hardness = 2.0 - 2.5 | |
| − | + | * Density = 2.6-2.63 g/ml | |
| − | + | * Refractive Index = 1.558; 1.565; 1.564 | |
| − | + | * Perfect cleavage in one direction. | |
| − | + | * Plastic when wet. Brittle when dry. | |
| − | + | * Fracture = earthy (friable). | |
| − | + | * Luster =dull to pearly. | |
| − | + | * Streak = white | |
| − | + | * Insoluble in water, cold acids and alkalis. | |
| − | + | * Monoclinic system with with hexagonal, plate-like crystals 0.1-1.0 micrometers. | |
| − | + | * Microscopically particles are translucent and colorless with moderate relief. Under crossed polars, particles have low birefringence. | |
| − | + | * Kaolin fluoresces a pale white. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
| − | [[media: | + | [[media:download_file_200.pdf|Properties of Common Abrasives]] |
| − | [[media: | + | [[media:download_file_512.pdf|Characteristics of Common White Pigments]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | == Resources and Citations == | ||
| + | * WebMinerals: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Kaolinite.shtml Kaolinite] | ||
* Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, ''Pigment Compendium'', Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004 | * Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, ''Pigment Compendium'', Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004 | ||
| − | |||
* R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 | * R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 | ||
| − | |||
* Ralph Mayer, ''A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques'', Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing) | * Ralph Mayer, ''A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques'', Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing) | ||
| − | |||
* Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, ''Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology'', U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982 | * Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, ''Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology'', U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982 | ||
| − | |||
* Robert Fournier, ''Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery'', Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992 | * Robert Fournier, ''Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery'', Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992 | ||
| − | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Kaolin." Accessed: 2 Sept. 2004. | |
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Kaolin." | + | * Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kaolinite Kaolinite] (Accessed Sept. 7, 2005 and March 2025) |
| − | |||
| − | * Wikipedia | ||
| − | |||
* Reed Kay, ''The Painter's Guide To Studio Methods and Materials'', Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1983 | * Reed Kay, ''The Painter's Guide To Studio Methods and Materials'', Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1983 | ||
| − | |||
* Tom Rowland, Noel Riley, ''A-Z Guide to Cleaning, Conserving and Repairing Antiques'', Constable and Co., Ltd., London, 1981 | * Tom Rowland, Noel Riley, ''A-Z Guide to Cleaning, Conserving and Repairing Antiques'', Constable and Co., Ltd., London, 1981 | ||
| − | |||
* Jack Odgen, ''Jewellery of the Ancient World'', Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982 | * Jack Odgen, ''Jewellery of the Ancient World'', Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982 | ||
| − | |||
* Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | ||
| − | |||
* ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
| − | |||
* Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | ||
| − | |||
* ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry #5294 | * ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry #5294 | ||
| − | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, | + | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000 |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:44, 12 March 2025
Description
A type of [[primary clay] formed by the weathering of aluminum silicates, such as feldspars and Nepheline. When pure, kaolin is a soft, white, absorbent powder composed primarily of the mineral Kaolinite, a hydrated aluminum silicate. Impurities, such as iron oxide, silica, and other minerals, can produce yellow, red, blue, gray, or brownish color clays. Kaolin occurs at many locations around the world (France, England, Germany, China, United States, etc.). Kaolin is used to produce fine quality Porcelain and china. It is also used as a base for lake colors and as a filler in paints, pastels, papers, rubbers, cements, and epoxies. Kaolin (as brick dust) has been used as an Abrasive for polishing Gold and other metals. It is also a useful Absorbent for oils and greases and has been used commercially for cleaning fabrics, furs, and carpets.
Synonyms and Related Terms
kaolinite; China clay; Devonshire clay; Pigment White 19; CI 77005; Kaolinit (Deut.); Satinkreide (Deut.); caolín (Esp.); kaoliini (Fin.); kaolin (Fr.); blanc de Chine (Fr.); kaolinis (Gr.); caolino (It.); terra bianca (It.); bolo bianco (It.); creta Eretria (old Roman); bolus alba (old Roman); kaolien (Ned.); caulino (Port.); satinkrita (Sven.); dkar po (Tibetan); bolus alba; porcelain clay; white bole; argilla; paper clay; brick dust; fuller's earth; white bolus; white heart; pipe clay; pipeclay;
Risks
- Noncombustible
- ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Composition = Al2Si2O5(OH4)
- Mohs Hardness = 2.0 - 2.5
- Density = 2.6-2.63 g/ml
- Refractive Index = 1.558; 1.565; 1.564
- Perfect cleavage in one direction.
- Plastic when wet. Brittle when dry.
- Fracture = earthy (friable).
- Luster =dull to pearly.
- Streak = white
- Insoluble in water, cold acids and alkalis.
- Monoclinic system with with hexagonal, plate-like crystals 0.1-1.0 micrometers.
- Microscopically particles are translucent and colorless with moderate relief. Under crossed polars, particles have low birefringence.
- Kaolin fluoresces a pale white.
Comparisons
Properties of Common Abrasives
Characteristics of Common White Pigments
Resources and Citations
- WebMinerals: Kaolinite
- Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, Pigment Compendium, Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Robert Fournier, Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery, Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Kaolin." Accessed: 2 Sept. 2004.
- Wikipedia: Kaolinite (Accessed Sept. 7, 2005 and March 2025)
- Reed Kay, The Painter's Guide To Studio Methods and Materials, Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1983
- Tom Rowland, Noel Riley, A-Z Guide to Cleaning, Conserving and Repairing Antiques, Constable and Co., Ltd., London, 1981
- Jack Odgen, Jewellery of the Ancient World, Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry #5294
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000