Difference between revisions of "PEM E80968 Dragon robe, China (19th century)"
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Artifact Information == | == Artifact Information == | ||
| + | The Peabody Essex Museum in Salem, MA USA. E80968. | ||
| + | |||
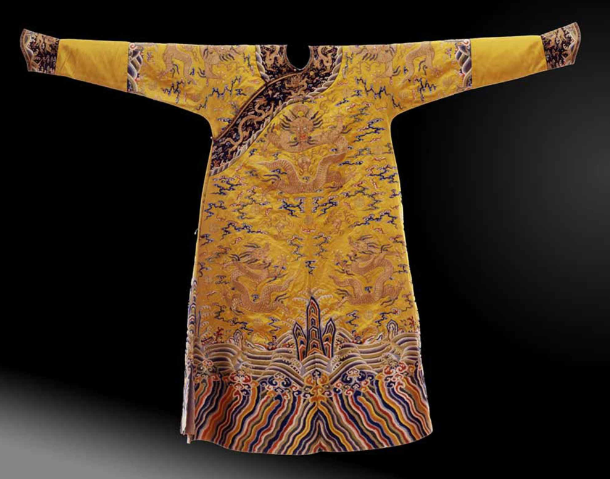
| + | The Peabody Essex Museum collected a dragon robe (E80968) thought to have been produced for the late Qing dynasty court. Beginning in the seventeenth century, only the emperor, empress, empress dowager and sometimes a high-ranking imperial consort were permitted to wear garments in | ||
| + | this ‘bright’ or ‘clear’ shade of yellow, known in Chinese as ming huang [1]. The robe was probably made for a very high-ranking woman at court, if not the Emperor’s wife or mother. The height of the lishui wave border at the hem, in addition to the prominence of the dragons, stylistically place this robe in the middle of the nineteenth century [2]. | ||
| − | The Peabody Essex Museum in Salem, MA USA. | + | [[File:80968.PNG|center|frame|Imperial dragon robe. © The Peabody Essex Museum in Salem, MA USA. ]] |
| − | + | == Summary of results == | |
| − | + | [[File:Sampling PEM E80968.PNG|thumb|'''One yellow thread from the collar seam was removed for dye analysis]] | |
| − | Yellow thread from the collar seam was samples and analyzed. The major components of the plant are flavonoids: rutin, keampferol and quecetin glycosides. The dyeing source was probably [http://cameo.mfa.org/wiki/Pagoda_tree_(Styphnolobium_japonicum)_LC pagoda tree buds]. | + | Yellow thread from the collar seam was samples and analyzed. The major components of the plant are flavonoids: rutin, keampferol and quecetin glycosides. The dyeing source was probably [http://cameo.mfa.org/wiki/Pagoda_tree_(Styphnolobium_japonicum)_LC pagoda tree buds]. [2] |
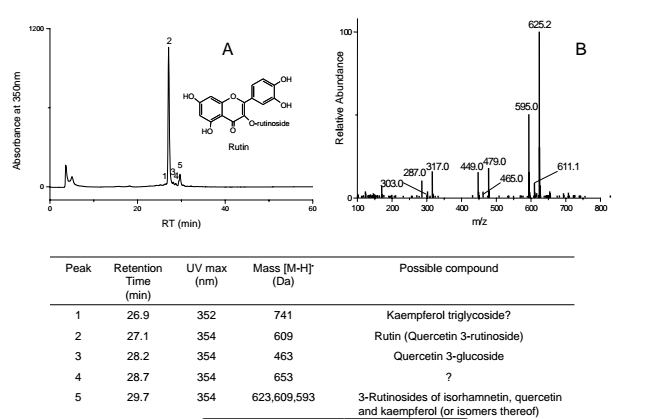
== HPLC profile == | == HPLC profile == | ||
| + | [[File:Pagoda tree historial sample.PNG|center|frame|HPLC-DAD profile, extract from the robe, Absorbance at 350nm (mAU) by X. Zhang]] | ||
| + | == References == | ||
| − | + | [1] Gary Dickinson, and Linda Wrigglesworth, Imperial Wardrobe, Bamboo Press, London, (1990) 199. | |
| − | [ | + | [2] Xian Zhang,Karina Corrigan, Bruce MacLaren, Mimi Leveque, and Richard A. Laursen, Characterization of Yellow Dyes in Nineteenth Century Chinese Textiles. Studies in Conservation 52, 211-220 (2007). |
Latest revision as of 09:05, 31 August 2017
Artifact Information
The Peabody Essex Museum in Salem, MA USA. E80968.
The Peabody Essex Museum collected a dragon robe (E80968) thought to have been produced for the late Qing dynasty court. Beginning in the seventeenth century, only the emperor, empress, empress dowager and sometimes a high-ranking imperial consort were permitted to wear garments in this ‘bright’ or ‘clear’ shade of yellow, known in Chinese as ming huang [1]. The robe was probably made for a very high-ranking woman at court, if not the Emperor’s wife or mother. The height of the lishui wave border at the hem, in addition to the prominence of the dragons, stylistically place this robe in the middle of the nineteenth century [2].
Summary of results
Yellow thread from the collar seam was samples and analyzed. The major components of the plant are flavonoids: rutin, keampferol and quecetin glycosides. The dyeing source was probably pagoda tree buds. [2]
HPLC profile
References
[1] Gary Dickinson, and Linda Wrigglesworth, Imperial Wardrobe, Bamboo Press, London, (1990) 199.
[2] Xian Zhang,Karina Corrigan, Bruce MacLaren, Mimi Leveque, and Richard A. Laursen, Characterization of Yellow Dyes in Nineteenth Century Chinese Textiles. Studies in Conservation 52, 211-220 (2007).