Difference between revisions of "Calcium stearate"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(username removed) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A waxy white powder first isolated for commercial use in 1924. Calcium stearate is used industrially as a [ | + | A waxy white powder first isolated for commercial use in 1924. Calcium stearate is used industrially as a [[flatting agent]] in [[paint|paints]], a waterproofing agent in [[cement|cements]], and as a solid-phase [[lubricant]] for [[plastic|plastics]]. For foods, calcium stearate is used as a bread dough conditioner, an [[emulsifier]], an anti-dusting agent, a [[thickening agent|thickener]], and as a [[release agent]]. |
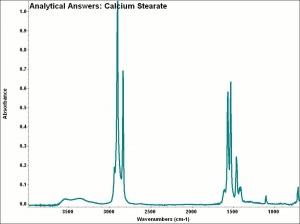
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiCA_STEAR.jpg~FTIR]]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
calcium octadecanoic acid; stearic acid calcium salt; | calcium octadecanoic acid; stearic acid calcium salt; | ||
| − | [ | + | == Risks == |
| + | |||
| + | * Available in technical and food grades. | ||
| + | * Combustible. | ||
| + | * ThermoFisher: [https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=AA39423A1&productDescription=CALCIUM+STEARATE+1KG&vendorId=VN00024248&countryCode=US&language=en SDS] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== |
| − | Insoluble in water, ether, chloroform, acetone and cold alcohol. Slight soluble in hot alcohol and hot oils. Soluble in hot | + | Insoluble in water, ether, chloroform, acetone and cold alcohol. Slight soluble in hot alcohol and hot oils. Soluble in hot pyridine. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 22: | Line 26: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 179 | + | | 179 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 1.04-1.12 | + | | 1.04-1.12 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 31: | Line 35: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 557 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 557 | ||
| − | * | + | * USDA website at http://www.ams.usda.gov/nop/NationalList/TAPReviews/CalciumStearate2.pdf (Accessed Sept 23, 2005) |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:24, 18 May 2022
Description
A waxy white powder first isolated for commercial use in 1924. Calcium stearate is used industrially as a Flatting agent in paints, a waterproofing agent in cements, and as a solid-phase Lubricant for plastics. For foods, calcium stearate is used as a bread dough conditioner, an Emulsifier, an anti-dusting agent, a thickener, and as a Release agent.
Synonyms and Related Terms
calcium octadecanoic acid; stearic acid calcium salt;
Risks
- Available in technical and food grades.
- Combustible.
- ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Insoluble in water, ether, chloroform, acetone and cold alcohol. Slight soluble in hot alcohol and hot oils. Soluble in hot pyridine.
| Composition | Ca(C18H35O2)2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 1592-23-0 |
| Melting Point | 179 C |
| Density | 1.04-1.12 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | 607.03 |
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 557
- USDA website at http://www.ams.usda.gov/nop/NationalList/TAPReviews/CalciumStearate2.pdf (Accessed Sept 23, 2005)