Difference between revisions of "Pyroxene"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(username removed) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | One of the major classes of silicate minerals. Pyroxenes, in general, a series of doubly hydrated silicates usually containing either calcium, magnesium, or iron. They are distinguished from [ | + | One of the major classes of silicate minerals. Pyroxenes, in general, a series of doubly hydrated silicates usually containing either calcium, magnesium, or iron. They are distinguished from [[amphibole|amphiboles]], a second major class, by their cleavage planes. Amphiboles have cleavage angles of 56 and 124 degrees while pyroxenes have cleavage angles of 5 and 93 degrees. Pyroxenes are commonly found in both [[igneous|igneous]] and [[metamorphic|metamorphic]] rocks. Examples of some [[augite|augite]], [[enstatite|enstatite]], [[diopside|diopside]], pyroxenite, [[jadeite|jadeite]], spudomene, and [[rhodonite|rhodonite]]. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | pyroxenite; Pyroxen (Deut.); piroxeno (Esp.); | + | pyroxenite; Pyroxen (Deut.); piroxeno (Esp.);pyroxène (Fr.); pyroxenen (Ned.); pirokseny (Pol.); piroxena (Port.); pyroxeen (Ned.) |
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | * | + | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 |
| − | * | + | * R.F.Symmes, T.T.Harding, Paul Taylor, ''Rocks, Fossils and Gems'', DK Publishing, Inc., New York City, 1997 |
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pyroxene (Accessed Nov. 9, 2005) |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:41, 20 August 2022
Description
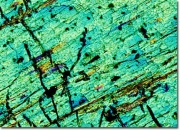
One of the major classes of silicate minerals. Pyroxenes, in general, a series of doubly hydrated silicates usually containing either calcium, magnesium, or iron. They are distinguished from amphiboles, a second major class, by their cleavage planes. Amphiboles have cleavage angles of 56 and 124 degrees while pyroxenes have cleavage angles of 5 and 93 degrees. Pyroxenes are commonly found in both Igneous and Metamorphic rocks. Examples of some Augite, Enstatite, Diopside, pyroxenite, Jadeite, spudomene, and Rhodonite.
Synonyms and Related Terms
pyroxenite; Pyroxen (Deut.); piroxeno (Esp.);pyroxène (Fr.); pyroxenen (Ned.); pirokseny (Pol.); piroxena (Port.); pyroxeen (Ned.)
Resources and Citations
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- R.F.Symmes, T.T.Harding, Paul Taylor, Rocks, Fossils and Gems, DK Publishing, Inc., New York City, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pyroxene (Accessed Nov. 9, 2005)