Difference between revisions of "Fluosilicic acid"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|fluosilicic acid.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|fluosilicic acid.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Risks == |
| − | Contact, inhalation or ingestion will cause severe corrosion of skin and mucous membranes. Avoid all contact. Non combustible. | + | * Contact, inhalation or ingestion will cause severe corrosion of skin and mucous membranes. |
| + | * Avoid all contact. | ||
| + | * Non combustible. | ||
| + | * CDC Fine Chemicals: [https://www.cdhfinechemical.com/images/product/msds/5_1953120203_FLUOSILICICACID-CASNO-16961-83-4-MSDS.pdf SDS] | ||
| − | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | |
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
Miscible in water. | Miscible in water. | ||
Latest revision as of 15:10, 21 August 2022
Description
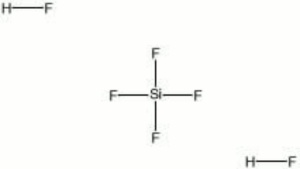
A colorless, fuming liquid that is available as an aqueous solution. In water, SiF4 and HF combine to form fluosilicic acid. It is a strong acid that will attack Glass and stoneware. Dilute solutions (1-2%) are used for sterilizing bottles, disinfecting copper and brass vessels, as well as for killing fungus on wood, masonry, and Plaster. Fluosilicic acid is also used for fluoridating water, cleaning Leather, and for hardening Cement, and Lime.
Synonyms and Related Terms
fluorosilicic acid; hydrogen hexafluorosilicate; hexafluosilicic acid; hydrosilicofluoric acid; hydrofluosilicic acid; silicofluoric acid;
Risks
- Contact, inhalation or ingestion will cause severe corrosion of skin and mucous membranes.
- Avoid all contact.
- Non combustible.
- CDC Fine Chemicals: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Miscible in water.
| Composition | H2SiF6 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 16961-83-4 |
| Melting Point | (dec) |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 144.1 |
Resources and Citations
- Thomas Gregory, The Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Reinhold Publishing, New York, 3rd ed., 1942
- Hermann Kuhn, Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities, Butterworths, London, 1986
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 4220
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997