Difference between revisions of "Lemon yellow"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (7 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
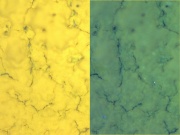
| − | [[File:Lemonyellow C100x.jpg|thumb|Lemon yellow ( | + | [[File:Lemonyellow C100x.jpg|thumb|Lemon yellow on alum; photos at 100x (visible light on left; UV light on right)]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | An unstandardized pigment name that is more associated with the color hue. Lemon yellow may contain one or more of the following yellow pigments: [ | + | An unstandardized pigment name that is more associated with the color hue. Lemon yellow may contain one or more of the following yellow pigments: [[barium chromate]], [[strontium chromate]], [[zinc yellow|zinc chromate]]. The name has also been used for yellow organic colorants. Lemon yellow was also called as ultramarine yellow. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
ultramarine yellow; zinc chromate; barium chromate; strontium chromate; amarillo limón (Esp.); jaune citron (Fr.); amarelo limão (Port.) | ultramarine yellow; zinc chromate; barium chromate; strontium chromate; amarillo limón (Esp.); jaune citron (Fr.); amarelo limão (Port.) | ||
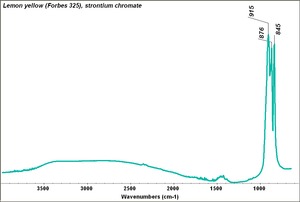
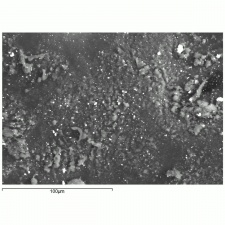
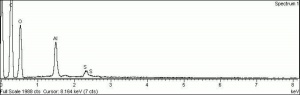
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|f326sem.jpg~SEM|f327sem.jpg~SEM|f326edsbw.jpg~EDS|f327edsbw.jpg~EDS|Slide34 FC324.PNG~XRF]]] | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Lemon yellow 325.TIF~FTIR (MFA)|Lemon yellow (Forbes MFA 325) 50X, 532 nm (640x445).jpg~Raman (MFA)|f326sem.jpg~SEM|f327sem.jpg~SEM|f326edsbw.jpg~EDS|f327edsbw.jpg~EDS|Slide34 FC324.PNG~XRF]]] |
| − | == | + | == Risks == |
| − | Human carcinogen. Skin contact may cause allergies. Acute ingestion may cause fatal chromium poisoning. Chronic inhalation may cause lung cancer and respiratory irritation. Combustible. | + | * Human carcinogen. |
| + | * Skin contact may cause allergies. | ||
| + | * Acute ingestion may cause fatal chromium poisoning. | ||
| + | * Chronic inhalation may cause lung cancer and respiratory irritation. Combustible. | ||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
* R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 | * R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 | ||
| Line 24: | Line 27: | ||
* R.D. Harley, ''Artists' Pigments c. 1600-1835'', Butterworth Scientific, London, 1982 | * R.D. Harley, ''Artists' Pigments c. 1600-1835'', Butterworth Scientific, London, 1982 | ||
| − | * | + | * Pigments Through the Ages - http://webexhibits.org/pigments/indiv/overview/leadwhite.html = barium yellow |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:08, 7 October 2022
Description
An unstandardized pigment name that is more associated with the color hue. Lemon yellow may contain one or more of the following yellow pigments: Barium chromate, Strontium chromate, zinc chromate. The name has also been used for yellow organic colorants. Lemon yellow was also called as ultramarine yellow.
Synonyms and Related Terms
ultramarine yellow; zinc chromate; barium chromate; strontium chromate; amarillo limón (Esp.); jaune citron (Fr.); amarelo limão (Port.)
Risks
- Human carcinogen.
- Skin contact may cause allergies.
- Acute ingestion may cause fatal chromium poisoning.
- Chronic inhalation may cause lung cancer and respiratory irritation. Combustible.
Resources and Citations
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- R.D. Harley, Artists' Pigments c. 1600-1835, Butterworth Scientific, London, 1982
- Pigments Through the Ages - http://webexhibits.org/pigments/indiv/overview/leadwhite.html = barium yellow