Difference between revisions of "Chalcopyrite"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
copper pyrite; peacock ore; yellow copper; copper yellow; Chalcopyrit (Deut.); Chalkopyrit (Deut.); Kupferkies (Deut.); calcopirita (Esp.); chalcopyrite (Fr.); chalcopyriet (Ned.); calcopirite (Port.) | copper pyrite; peacock ore; yellow copper; copper yellow; Chalcopyrit (Deut.); Chalkopyrit (Deut.); Kupferkies (Deut.); calcopirita (Esp.); chalcopyrite (Fr.); chalcopyriet (Ned.); calcopirite (Port.) | ||
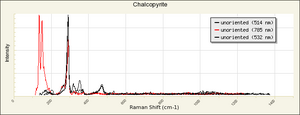
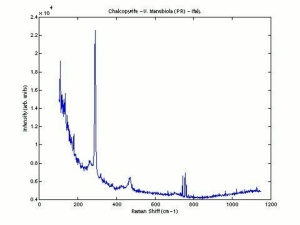
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Chalcopyriteitaly2.jpg~Raman]]] | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Chalcopyrite Raman RRUFF R050018.png~Raman (RRUFF)|Chalcopyriteitaly2.jpg~Raman (U of Parma)]]] |
| − | |||
== Physical and Chemical Properties == | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
| − | Tetragonal crystal system, often with repeated twinning. Fracture = uneven, brittle. Luster = metallic. Streak =greenish-black. Soluble in nitric acid. Magnetic on heating | + | * Tetragonal crystal system, often with repeated twinning. |
| + | * Fracture = uneven, brittle. | ||
| + | * Luster = metallic. | ||
| + | * Streak =greenish-black. | ||
| + | * Soluble in nitric acid. | ||
| + | * Magnetic on heating | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
Latest revision as of 12:06, 6 December 2022
Description
A common mineral composed of copper iron sulfide. Chalcopyrite has brassy yellow crystals with a metallic luster and greenish or purplish iridescence. Chalcopyrite is an important source for Copper and is mined in Canada (Ontario, Quebec, British Columbia), Chile, Peru, Bolivia, Japan (Ani), England (Cornwall), Germany (Saxony), France (Alsace), Spain (Rio Tinto) and the U.S. (Montana, Arizona, Utah, Tennessee, Missouri, Wisconsin).
Synonyms and Related Terms
copper pyrite; peacock ore; yellow copper; copper yellow; Chalcopyrit (Deut.); Chalkopyrit (Deut.); Kupferkies (Deut.); calcopirita (Esp.); chalcopyrite (Fr.); chalcopyriet (Ned.); calcopirite (Port.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Tetragonal crystal system, often with repeated twinning.
- Fracture = uneven, brittle.
- Luster = metallic.
- Streak =greenish-black.
- Soluble in nitric acid.
- Magnetic on heating
| Composition | CuFeS2 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 3.5 - 4.0 |
| Melting Point | 950 C |
| Density | 4.1-4.3 g/ml |
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Chalcopyrite
- Robert Fournier, Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery, Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "chalcopyrite" [Accessed December 11, 2001].
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chalcopyrite (accessed Sept. 2, 2005)
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 231
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998