Difference between revisions of "Rose quartz"
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:36.187-SC109787.jpg|thumb|Babylonian seal<br>MFA# 36.187]] | [[File:36.187-SC109787.jpg|thumb|Babylonian seal<br>MFA# 36.187]] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | + | [[File:63.288-SC16017.jpg|thumb|Rose quartz pendant]] | |
A pink [[quartz|quartz]] used as a [[gemstone|gemstone]] and ornamental stone. Rose quartz has been mined or gathered since the early iron age (1200-500 BCE). It is found in the Ural Mountains, Czech Republic, Germany (Bavaria), Scotland, Ireland, Sweden, Italy, India, Madagascar, Namibia, Brazil (Minas Gerais), and the U.S.(South Dakota, California, Montana, South Dakota, Maine). Rose quartz ranges in color from a pale pink to a deep rose red. Transparent rose quartz is used as a gemstone while translucent varieties have been used for vases, ornaments and architectural elements. Some rose quartz may have needlelike inclusions of [[rutile|rutile]] that induce a star-shaped [[chatoyant|chatoyancy]]. | A pink [[quartz|quartz]] used as a [[gemstone|gemstone]] and ornamental stone. Rose quartz has been mined or gathered since the early iron age (1200-500 BCE). It is found in the Ural Mountains, Czech Republic, Germany (Bavaria), Scotland, Ireland, Sweden, Italy, India, Madagascar, Namibia, Brazil (Minas Gerais), and the U.S.(South Dakota, California, Montana, South Dakota, Maine). Rose quartz ranges in color from a pale pink to a deep rose red. Transparent rose quartz is used as a gemstone while translucent varieties have been used for vases, ornaments and architectural elements. Some rose quartz may have needlelike inclusions of [[rutile|rutile]] that induce a star-shaped [[chatoyant|chatoyancy]]. | ||
| − | |||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
quartz; Rosenquarz (Deut.); cuarzo rosa (Esp.); quartz rose (Fr.); quartzo roseo (Port.); Rosenquarz (Deut.); roze kwarts (Ned.) | quartz; Rosenquarz (Deut.); cuarzo rosa (Esp.); quartz rose (Fr.); quartzo roseo (Port.); Rosenquarz (Deut.); roze kwarts (Ned.) | ||
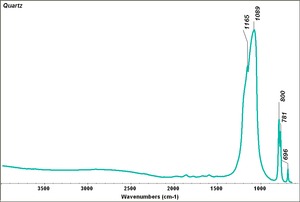
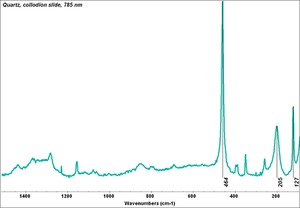
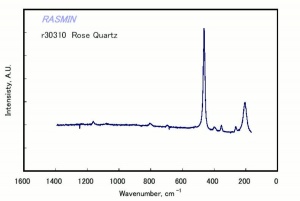
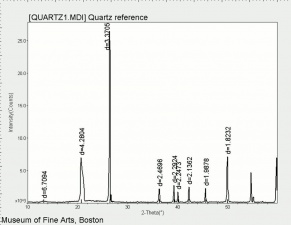
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|rosequartzRS.jpg~Raman]]] | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Quartz.TIF~FTIR (MFA)|Quartz, collodion slide, 785 nm copy.tif~Raman (MFA)|rosequartzRS.jpg~Raman (Rasmin)|QUARTZ1.jpg~XRD (MFA)]]] |
== Physical and Chemical Properties == | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
| − | Trigonal crystal system | + | * Trigonal crystal system |
| − | + | * Low thermal expansion | |
| − | Fracture = conchoidal | + | * Fracture = conchoidal |
| + | * Luster = vitreous to greasy | ||
| + | * Streak = white | ||
| + | * Fluorescence = inert to weak purple under SW | ||
| + | * Pleochroism = none | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 26: | Line 29: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 2.65 | + | | 2.65 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ||
| − | | 1. | + | | 1.544 - 1.553 |
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row"| Birefringence | ||
| + | | 0.009 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
[[media:download_file_435.pdf|Properties of Common Gemstones]] | [[media:download_file_435.pdf|Properties of Common Gemstones]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Additional Images == | == Additional Images == | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
File:Rosenquarzkes.jpg|Rose quartz | File:Rosenquarzkes.jpg|Rose quartz | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | |||
==Resources and Citations== | ==Resources and Citations== | ||
| + | * Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016. | ||
* Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Quartz.shtml Quartz] | * Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Quartz.shtml Quartz] | ||
| − | |||
* Jack Odgen, ''Jewellery of the Ancient World'', Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982 | * Jack Odgen, ''Jewellery of the Ancient World'', Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982 | ||
| − | |||
* A.Lucas, J.R.Harris, ''Ancient Egyptian Materials and Industries'', Edward Arnold Publishers Ltd., London, 4th edition, 1962 | * A.Lucas, J.R.Harris, ''Ancient Egyptian Materials and Industries'', Edward Arnold Publishers Ltd., London, 4th edition, 1962 | ||
| − | |||
* ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "rose quartz." Accessed: 14 Sept. 2001 . | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "rose quartz." Accessed: 14 Sept. 2001 . | ||
| − | |||
* C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | * C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | ||
| − | |||
* Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rose_quartz (Accessed Sept. 14, 2005) | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rose_quartz (Accessed Sept. 14, 2005) | ||
| − | |||
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p.647 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p.647 | ||
| − | |||
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
Latest revision as of 10:00, 16 December 2022
Description
A pink Quartz used as a Gemstone and ornamental stone. Rose quartz has been mined or gathered since the early iron age (1200-500 BCE). It is found in the Ural Mountains, Czech Republic, Germany (Bavaria), Scotland, Ireland, Sweden, Italy, India, Madagascar, Namibia, Brazil (Minas Gerais), and the U.S.(South Dakota, California, Montana, South Dakota, Maine). Rose quartz ranges in color from a pale pink to a deep rose red. Transparent rose quartz is used as a gemstone while translucent varieties have been used for vases, ornaments and architectural elements. Some rose quartz may have needlelike inclusions of Rutile that induce a star-shaped chatoyancy.
Synonyms and Related Terms
quartz; Rosenquarz (Deut.); cuarzo rosa (Esp.); quartz rose (Fr.); quartzo roseo (Port.); Rosenquarz (Deut.); roze kwarts (Ned.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Trigonal crystal system
- Low thermal expansion
- Fracture = conchoidal
- Luster = vitreous to greasy
- Streak = white
- Fluorescence = inert to weak purple under SW
- Pleochroism = none
| Composition | SiO2 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 7.0 |
| Density | 2.65 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.544 - 1.553 |
| Birefringence | 0.009 |
Comparisons
Properties of Common Gemstones
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016.
- Mineralogy Database: Quartz
- Jack Odgen, Jewellery of the Ancient World, Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982
- A.Lucas, J.R.Harris, Ancient Egyptian Materials and Industries, Edward Arnold Publishers Ltd., London, 4th edition, 1962
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "rose quartz." Accessed: 14 Sept. 2001 .
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rose_quartz (Accessed Sept. 14, 2005)
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p.647
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998