Difference between revisions of "Sandwich panel"
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Aluminium composite material.png|thumb|Diagram of a sandwich panel structure uploaded from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sandwich_panel#/media/File:Aluminium_composite_material.png Wikimedia]]] | [[File:Aluminium composite material.png|thumb|Diagram of a sandwich panel structure uploaded from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sandwich_panel#/media/File:Aluminium_composite_material.png Wikimedia]]] | ||
[[File:FomeCor.jpg|thumb|Fome-Cor]] | [[File:FomeCor.jpg|thumb|Fome-Cor]] | ||
| + | [[File:archpaperhoneycomb side.jpg|thumb|Archival honeycomb board]] | ||
| + | [[File:Sandwich-Panel-Example.jpg|thumb|Multi-layer sandwich board diagram from [https://www.panelbuilt.com/blog/what-are-sandwich-panels Panel Built.com]]] | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| − | A special class of composite materials that is fabricated by attaching two thin, stiff skins to a lightweight core. The core material is normally of low strength, but its greater thickness provides a sandwich composite that has high bending stiffness but low density. | + | A special class of composite materials that is fabricated by attaching two thin, stiff skins to a lightweight core. The core material is normally of low strength, but its greater thickness provides a sandwich composite that has high bending stiffness but low density. Commonly used core materials include foams ([[Polyether sulfone|polyethersulfone]], [[Polyvinyl chloride|polyvinylchloride]], [[polyurethane]], [[polyethylene]], [[polystyrene]]), balsa wood, gypsum; fiberglass, corrugated sheets, and honeycombs (paper, aluminum, aramid). The skin material may be sheets of paper, cloth, metal, glass, carbon fiber or polymeric. Sandwich panels are used in applications to provide a combination of high structural rigidity and low weight. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
Latest revision as of 14:40, 7 February 2024
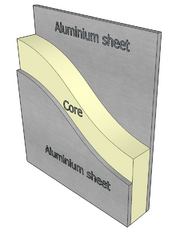

Description
A special class of composite materials that is fabricated by attaching two thin, stiff skins to a lightweight core. The core material is normally of low strength, but its greater thickness provides a sandwich composite that has high bending stiffness but low density. Commonly used core materials include foams (polyethersulfone, polyvinylchloride, Polyurethane, Polyethylene, Polystyrene), balsa wood, gypsum; fiberglass, corrugated sheets, and honeycombs (paper, aluminum, aramid). The skin material may be sheets of paper, cloth, metal, glass, carbon fiber or polymeric. Sandwich panels are used in applications to provide a combination of high structural rigidity and low weight.
Synonyms and Related Terms
sandwich board; sandwich plate; support board; foam core; composite board; sandwich-structure composite; honeycomb panel
Applications
- Construction
Working Properties
Risks
Forms and Sizes
Physical and Chemical Properties
Resources and Citations
- Wikipedia: Sandwich panel

