Difference between revisions of "Sodium chlorite"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(username removed) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | White, slightly hygroscopic crystals. Sodium chlorite is a powerful oxidizing agent. A dilute aqueous solution produces chlorous acid which is used as a mild [ | + | White, slightly hygroscopic crystals. Sodium chlorite is a powerful oxidizing agent. A dilute aqueous solution produces chlorous acid which is used as a mild [[bleaching%20agent|bleaching agent]] for textiles. Sodium chlorite is also used for the dilignification of paper pulp. |
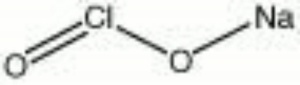
| + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|sodium chlorite.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Risks == | ||
| − | [ | + | * Very strong oxidizer. |
| + | * Fire and explosion hazard in contact with organic materials. | ||
| + | * Highly corrosive to tissues. | ||
| + | * Causes corrosion and burns. | ||
| + | * ThermoFisher: [https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=AC223235000&productDescription=SODIUM+CHLORITE%2C+TECH.%2C+500GR&vendorId=VN00033901&countryCode=US&language=en SDS] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== |
Soluble in water. | Soluble in water. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 25: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 180-200 (dec) | + | | 180-200 C (dec) |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 24: | Line 31: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 686 |
| − | * | + | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 |
| − | * | + | * Hermann Kuhn, ''Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities'', Butterworths, London, 1986 |
| − | * | + | * Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, ''Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology'', U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982 |
* ''The Dictionary of Paper'', American Paper Institute, New York, Fourth Edition, 1980 | * ''The Dictionary of Paper'', American Paper Institute, New York, Fourth Edition, 1980 | ||
Latest revision as of 14:48, 1 June 2022
Description
White, slightly hygroscopic crystals. Sodium chlorite is a powerful oxidizing agent. A dilute aqueous solution produces chlorous acid which is used as a mild Bleaching agent for textiles. Sodium chlorite is also used for the dilignification of paper pulp.
Risks
- Very strong oxidizer.
- Fire and explosion hazard in contact with organic materials.
- Highly corrosive to tissues.
- Causes corrosion and burns.
- ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in water.
| Composition | NaClO2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 7758-19-2 |
| Melting Point | 180-200 C (dec) |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 90.44 |
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 686
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Hermann Kuhn, Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities, Butterworths, London, 1986
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- The Dictionary of Paper, American Paper Institute, New York, Fourth Edition, 1980
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 8793