Difference between revisions of "Garnet"
| (16 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:21.1213-CR2071-d1.jpg|thumb|]] | + | [[File:21.1213-CR2071-d1.jpg|thumb|Carved garnet gem<br>MFA# 21.1213]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | + | [[File:Garnetemr2.jpg|thumb|Garnet]] | |
A family of minerals composed of trisilicates with [[aluminum]], [[iron]], [[calcium]], [[magnesium]], [[manganese]], or [[chromium]]. Garnets are found in deposits around the world as transparent crystals embedded in igneous and metamorphic rocks. They have been used as gemstones since antiquity. The ruby red [[pyrope]] and the lighter red [[almandine]] were the most highly prized varieties. The pale rose-purple [[rhodolite]] is a mixture of pyrope and almandine. Garnets are also used as abrasives. The crushed, ground and cleaned garnet is sold as an abrasive powder, coated paper and coated cloth. Garnet particles have sharper cutting edges than aluminum oxide, but are expensive. To decrease costs, some commercially available garnet cloths are actually prepared with quartz. Sources of gem quality garnets include the Czech Republic, South Africa, Australia, China, India, Brazil, Sri Lanka, and the U.S (New York, Maine, Idaho). | A family of minerals composed of trisilicates with [[aluminum]], [[iron]], [[calcium]], [[magnesium]], [[manganese]], or [[chromium]]. Garnets are found in deposits around the world as transparent crystals embedded in igneous and metamorphic rocks. They have been used as gemstones since antiquity. The ruby red [[pyrope]] and the lighter red [[almandine]] were the most highly prized varieties. The pale rose-purple [[rhodolite]] is a mixture of pyrope and almandine. Garnets are also used as abrasives. The crushed, ground and cleaned garnet is sold as an abrasive powder, coated paper and coated cloth. Garnet particles have sharper cutting edges than aluminum oxide, but are expensive. To decrease costs, some commercially available garnet cloths are actually prepared with quartz. Sources of gem quality garnets include the Czech Republic, South Africa, Australia, China, India, Brazil, Sri Lanka, and the U.S (New York, Maine, Idaho). | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Garnetemr3.jpg|thumb|Garnet]] |
| − | |||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | pyrope (deep red to black); almandine ( | + | pyrope (deep red to black); almandine (bright red to black); spessartine (orange to red to brown); grossularite (green); grossular (colorless); carbuncle; andradite (wine red); uvarovite (emerald green); tsavorite (green); rhodolite (pale red to purple); hessonite (golden); topazolite; demantoid; melanite; Uralian emeralds; Greek anthrax; Granat (Deut.); granate (Esp.); grenat (Fr.); granaat (Ned.); granada (Port.); granatus (Lat.) |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
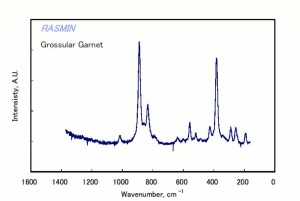
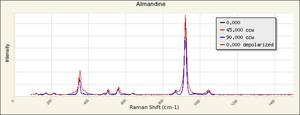
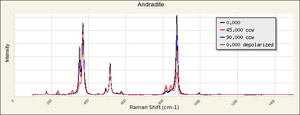
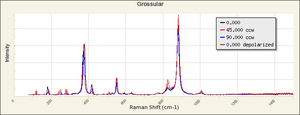
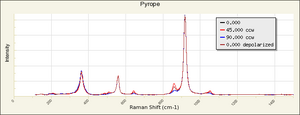
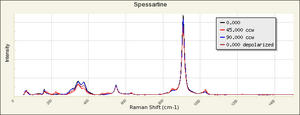
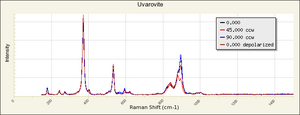
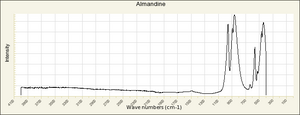
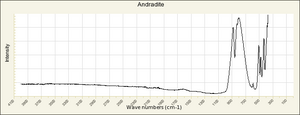
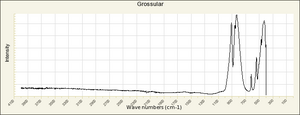
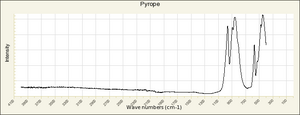
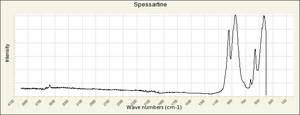
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|garnetgrossRS.jpg~Raman of Grossular (RASMIN)|Almandine Raman RRUFF R040079.png~Raman of Almandine (RRUFF)|Andradite Raman RRUFF R040001.png~Raman of Andradite (RRUFF)|Grossular Raman RRUFF R040065.png~Raman of Grossular (RRUFF)|Pyrope raman RRUFF R040159.png~Raman of Pyrope (RRUFF)|Spessartine Raman RRUFF R050063.png~Raman of Spessartine (RRUFF)|Uvarovite Raman RRUFF R061041.png~Raman of Uvarovite (RRUFF)]]] | |
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Almandine IR-ATR R040079.png~IR-ATR of Almandine (RRUFF)|Andradite Infrared RRUFF R040001.png~IR-ATR of Andradite (RRUFF)|Grossular IR-ATR RRUFF R040065.png~IR-ATR of Grossular (RRUFF)|Pyrope IR-ATR R040159.png|Spessartine IR-ATR RRUFF R050063.png~IR-ATR of Spessartine (RRUFF)|Uvarovite IR-ATR RRUFF R061041.png~IR-ATR of Uvarovite (RRUFF)]]] | |
| + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ||
| − | Fluorescence = none (except green | + | * Isometric crystal system with dodecahedron and trapezohedron habits |
| + | * Luster = vitreous to resinous | ||
| + | * Fracture = conchoidal or uneven | ||
| + | * Cleavage = indistinct | ||
| + | * Streak = colorless to white | ||
| + | * Fluorescence = none (except green or yellow stones that may give weak yellow-orange colors in LW and SW) | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 26: | Line 27: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 3.52-4.32 | + | | 3.52-4.32 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ||
| − | | 1. | + | | 1.72-1.94 |
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row"| Birefringence | ||
| + | | none | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
[[media:download_file_413.pdf|Natural and Simulated Diamonds]] | [[media:download_file_413.pdf|Natural and Simulated Diamonds]] | ||
| − | + | ==Resources and Citations== | |
| − | + | * Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016. | |
| − | == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Jack Odgen, ''Jewellery of the Ancient World'', Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982 | * Jack Odgen, ''Jewellery of the Ancient World'', Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982 | ||
| − | |||
* R.F.Symmes, T.T.Harding, Paul Taylor, ''Rocks, Fossils and Gems'', DK Publishing, Inc., New York City, 1997 | * R.F.Symmes, T.T.Harding, Paul Taylor, ''Rocks, Fossils and Gems'', DK Publishing, Inc., New York City, 1997 | ||
| − | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "garnet" [Accessed December 4, 2001]. (color photo) | |
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "garnet" | ||
| − | |||
* C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | * C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | ||
| − | |||
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: Mohs hardness = 8 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: Mohs hardness = 8 | ||
| − | |||
* ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
| − | + | * Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Garnet Garnet] (Accessed Sept. 7, 2005 and Dec 2022) | |
| − | * Wikipedia | ||
| − | |||
* ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics'', Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=3.15-4.3 | * ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics'', Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=3.15-4.3 | ||
| − | |||
* R.M.Organ, ''Design for Scientific Conservation of Antiquities'', Smithsonian Institution, Washington DC, 1968 | * R.M.Organ, ''Design for Scientific Conservation of Antiquities'', Smithsonian Institution, Washington DC, 1968 | ||
| − | |||
* Michael McCann, ''Artist Beware'', Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979 | * Michael McCann, ''Artist Beware'', Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979 | ||
Latest revision as of 12:01, 23 December 2022
Description
A family of minerals composed of trisilicates with Aluminum, Iron, Calcium, Magnesium, Manganese, or Chromium. Garnets are found in deposits around the world as transparent crystals embedded in igneous and metamorphic rocks. They have been used as gemstones since antiquity. The ruby red Pyrope and the lighter red Almandine were the most highly prized varieties. The pale rose-purple Rhodolite is a mixture of pyrope and almandine. Garnets are also used as abrasives. The crushed, ground and cleaned garnet is sold as an abrasive powder, coated paper and coated cloth. Garnet particles have sharper cutting edges than aluminum oxide, but are expensive. To decrease costs, some commercially available garnet cloths are actually prepared with quartz. Sources of gem quality garnets include the Czech Republic, South Africa, Australia, China, India, Brazil, Sri Lanka, and the U.S (New York, Maine, Idaho).
Synonyms and Related Terms
pyrope (deep red to black); almandine (bright red to black); spessartine (orange to red to brown); grossularite (green); grossular (colorless); carbuncle; andradite (wine red); uvarovite (emerald green); tsavorite (green); rhodolite (pale red to purple); hessonite (golden); topazolite; demantoid; melanite; Uralian emeralds; Greek anthrax; Granat (Deut.); granate (Esp.); grenat (Fr.); granaat (Ned.); granada (Port.); granatus (Lat.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Isometric crystal system with dodecahedron and trapezohedron habits
- Luster = vitreous to resinous
- Fracture = conchoidal or uneven
- Cleavage = indistinct
- Streak = colorless to white
- Fluorescence = none (except green or yellow stones that may give weak yellow-orange colors in LW and SW)
| Mohs Hardness | 6.5 - 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Density | 3.52-4.32 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.72-1.94 |
| Birefringence | none |
Comparisons
Properties of Common Abrasives
Properties of Common Gemstones
Natural and Simulated Diamonds
Resources and Citations
- Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016.
- Jack Odgen, Jewellery of the Ancient World, Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982
- R.F.Symmes, T.T.Harding, Paul Taylor, Rocks, Fossils and Gems, DK Publishing, Inc., New York City, 1997
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "garnet" [Accessed December 4, 2001]. (color photo)
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: Mohs hardness = 8
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Wikipedia: Garnet (Accessed Sept. 7, 2005 and Dec 2022)
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=3.15-4.3
- R.M.Organ, Design for Scientific Conservation of Antiquities, Smithsonian Institution, Washington DC, 1968
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979