Difference between revisions of "Klucel"
| (10 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | [Aqualon division of Hercules] A registered trademark for a series of hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) compounds. Klucel® polymers are nonionic, water soluble, ethers of cellulose. They produce solutions that range in viscosity from 200 to 2500 centipoise. The [[thermoplastic]] polymers are used as [[emulsifier|emulsifiers]], [[stabilizer|stabilizers]], film formers, [[thickening agent|thickeners]], and [[sealant|sealants]] in many types of solutions such as foods, cosmetics, [[paint remover|strippers]], [[paint|paints]] and [[glaze|glazes]]. They are also used as binders for ceramic glazes. Klucel® polymers also used as a [[size|sizing agents]] for [[paper]] and [[consolidant|consolidants]] for [[leather]]. While HPC polymers, in general, have good [[light stability|photochemical stability]], they can exhibit poor [[thermal stability]] and [[discoloration|discolor]] with age. Although the low molecular weight products, such as Klucel® G, performed better than the high molecular weight products, such as Klucel® M, testing indicates that HPC polymers should not be considered for long term use (Feller and Wilt 1990). | + | [formerly Aqualon division of Hercules] A registered trademark for a series of hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) compounds. Klucel® polymers are nonionic, water soluble, ethers of cellulose. They produce solutions that range in viscosity from 200 to 2500 centipoise. The [[thermoplastic]] polymers are used as [[emulsifier|emulsifiers]], [[stabilizer|stabilizers]], film formers, [[thickening agent|thickeners]], and [[sealant|sealants]] in many types of solutions such as foods, cosmetics, [[paint remover|strippers]], [[paint|paints]] and [[glaze|glazes]]. They are also used as binders for ceramic glazes. Klucel® polymers also used as a [[size|sizing agents]] for [[paper]] and [[consolidant|consolidants]] for [[leather]]. While HPC polymers, in general, have good [[light stability|photochemical stability]], they can exhibit poor [[thermal stability]] and [[discoloration|discolor]] with age. Although the low molecular weight products, such as Klucel® G, performed better than the high molecular weight products, such as Klucel® M, testing indicates that HPC polymers should not be considered for long term use (Feller and Wilt 1990). |
| + | |||
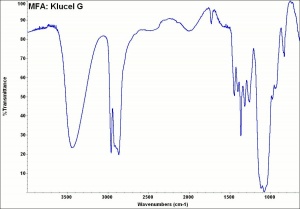
| + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|MFA- Klucel G.jpg~FTIR]]] | ||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 8: | Line 10: | ||
hydroxypropyl cellulose; Klucel® GF | hydroxypropyl cellulose; Klucel® GF | ||
| − | [[ | + | == Risks == |
| − | + | * Kremer-Pigmente: [https://www.kremer-pigmente.com/elements/resources/products/files/63710_SDS.pdf Klucel M SDS (dated 2017)] | |
| − | + | * University Products: [https://www.jerrysartarama.com/media/pdfs/lineco/klucel-g-sds-2019.pdf Klucel G SDS (dated 2018)] | |
| + | * Conservation by Design: [https://safety365.sevron.co.uk/substances/accessSDS/SDS-62925-579a142f66e165.01213856 Klucel MSDS (dated 1996)] | ||
| − | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | |
| − | Insoluble in water (above 45C). | + | * Soluble in water (below 38C), ethanol, acetone and many organic solvents. |
| + | * Insoluble in water (above 45C). | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | + | * Ashland: [https://www.ashland.com/industries/pharmaceutical/oral-solid-dose/klucel-hydroxypropylcellulose# Klucel Website] | |
| − | + | * R.Feller, M.Wilt, ''Evaluation of Cellulose Ethers for Conservation'', in Research in Conservation Series, Getty Conservation Institute, 1990, p. 94. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Hermann Kuhn, ''Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities'', Butterworths, London, 1986 | * Hermann Kuhn, ''Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities'', Butterworths, London, 1986 | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
* Ceramics and Glass Conservation Section, List of Workshop Materials, The British Museum, London | * Ceramics and Glass Conservation Section, List of Workshop Materials, The British Museum, London | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:57, 19 April 2022
Description
[formerly Aqualon division of Hercules] A registered trademark for a series of hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) compounds. Klucel® polymers are nonionic, water soluble, ethers of cellulose. They produce solutions that range in viscosity from 200 to 2500 centipoise. The Thermoplastic polymers are used as emulsifiers, stabilizers, film formers, thickeners, and sealants in many types of solutions such as foods, cosmetics, strippers, paints and glazes. They are also used as binders for ceramic glazes. Klucel® polymers also used as a sizing agents for Paper and consolidants for Leather. While HPC polymers, in general, have good photochemical stability, they can exhibit poor Thermal stability and discolor with age. Although the low molecular weight products, such as Klucel® G, performed better than the high molecular weight products, such as Klucel® M, testing indicates that HPC polymers should not be considered for long term use (Feller and Wilt 1990).
Synonyms and Related Terms
hydroxypropyl cellulose; Klucel® GF
Risks
- Kremer-Pigmente: Klucel M SDS (dated 2017)
- University Products: Klucel G SDS (dated 2018)
- Conservation by Design: Klucel MSDS (dated 1996)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soluble in water (below 38C), ethanol, acetone and many organic solvents.
- Insoluble in water (above 45C).
Resources and Citations
- Ashland: Klucel Website
- R.Feller, M.Wilt, Evaluation of Cellulose Ethers for Conservation, in Research in Conservation Series, Getty Conservation Institute, 1990, p. 94.
- Hermann Kuhn, Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities, Butterworths, London, 1986
- Book and Paper Group, Paper Conservation Catalog, AIC, 1984, 1989
- Ceramics and Glass Conservation Section, List of Workshop Materials, The British Museum, London