Difference between revisions of "Camphor"
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
An aromatic crystalline compound with a sweet smell. Camphor is obtained from the steam distillation of the leaves and wood of the camphor laurel tree, ''Cinnamomum camphora'', native to southeast Asia. It forms a white waxy solid when purified by steam distillation and sublimation. Since the 1930s camphor has also been made synthetically. Camphor has been used as an insect repellent and as a vapor phase corrosion inhibitor for metals. It was also used in [[Celluloid]] as a plasticizer for [[cellulose nitrate]]. Camphor sublimes slowly as room temperature; once vaporized it can react with and soften many plastics. | An aromatic crystalline compound with a sweet smell. Camphor is obtained from the steam distillation of the leaves and wood of the camphor laurel tree, ''Cinnamomum camphora'', native to southeast Asia. It forms a white waxy solid when purified by steam distillation and sublimation. Since the 1930s camphor has also been made synthetically. Camphor has been used as an insect repellent and as a vapor phase corrosion inhibitor for metals. It was also used in [[Celluloid]] as a plasticizer for [[cellulose nitrate]]. Camphor sublimes slowly as room temperature; once vaporized it can react with and soften many plastics. | ||
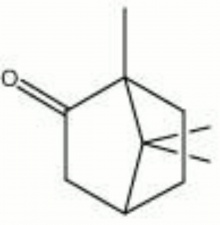
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|camphor.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
gum camphor; camphre (Fr.); 2-camphanone; 2-bornanone; Japan camphor; Formosa camphor; laurel camphor; synthetic camphor; Campher (Deut.); Kampfer(Deut.); camphre (Fr.); kamfer (Ned., Sven.); kamfora (Pol.); (Port.); | gum camphor; camphre (Fr.); 2-camphanone; 2-bornanone; Japan camphor; Formosa camphor; laurel camphor; synthetic camphor; Campher (Deut.); Kampfer(Deut.); camphre (Fr.); kamfer (Ned., Sven.); kamfora (Pol.); (Port.); | ||
| − | [ | + | == Risks == |
| + | |||
| + | * Combustible. Flash point = 64C | ||
| + | * Contact may cause irritation or burns. | ||
| + | * Ingestion can cause nausea, vomiting, vertigo, convulsions and death. | ||
| + | * Fisher Scientific: [https://fscimage.fishersci.com/msds/97150.htm MSDS] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== |
| − | Rhombohedral crystals. Sublimes at room temperature. Soluble in ethanol, ether, chloroform, aniline, nitrobenzene, carbon disulfide, decalin, ligroin. Slightly soluble in water (0.12 g in 100 ml). | + | * Rhombohedral crystals. |
| + | * Sublimes at room temperature. | ||
| + | * Soluble in ethanol, ether, chloroform, aniline, nitrobenzene, carbon disulfide, decalin, ligroin. Slightly soluble in water (0.12 g in 100 ml). | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 22: | Line 29: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 179.75 | + | | 179.75 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 0.992 | + | | 0.992 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 31: | Line 38: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Boiling Point | ! scope="row"| Boiling Point | ||
| − | | 204 | + | | 204 C |
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
| Line 54: | Line 53: | ||
* ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 | * ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 | ||
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "camphor" | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "camphor" [Accessed May 6, 2002]. |
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 134 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 134 | ||
| Line 70: | Line 69: | ||
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
| − | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, | + | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000 |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:46, 18 May 2022
Description
An aromatic crystalline compound with a sweet smell. Camphor is obtained from the steam distillation of the leaves and wood of the camphor laurel tree, Cinnamomum camphora, native to southeast Asia. It forms a white waxy solid when purified by steam distillation and sublimation. Since the 1930s camphor has also been made synthetically. Camphor has been used as an insect repellent and as a vapor phase corrosion inhibitor for metals. It was also used in Celluloid as a plasticizer for Cellulose nitrate. Camphor sublimes slowly as room temperature; once vaporized it can react with and soften many plastics.
Synonyms and Related Terms
gum camphor; camphre (Fr.); 2-camphanone; 2-bornanone; Japan camphor; Formosa camphor; laurel camphor; synthetic camphor; Campher (Deut.); Kampfer(Deut.); camphre (Fr.); kamfer (Ned., Sven.); kamfora (Pol.); (Port.);
Risks
- Combustible. Flash point = 64C
- Contact may cause irritation or burns.
- Ingestion can cause nausea, vomiting, vertigo, convulsions and death.
- Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Rhombohedral crystals.
- Sublimes at room temperature.
- Soluble in ethanol, ether, chloroform, aniline, nitrobenzene, carbon disulfide, decalin, ligroin. Slightly soluble in water (0.12 g in 100 ml).
| Composition | C10H16O |
|---|---|
| CAS | 76-22-2 |
| Melting Point | 179.75 C |
| Density | 0.992 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 152.23 |
| Boiling Point | 204 C |
Resources and Citations
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- MSDS Sheet Comment: Fisher Scientific 8/02/02: mp = 175-177 C, flash point = 64C
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "camphor" [Accessed May 6, 2002].
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 134
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Lynda A. Zycherman, J.Richard Schrock, A Guide to Museum Pest Control, FAIC and Association of Systematics Collections, Washington DC, 1988
- Pam Hatchfield, Pollutants in the Museum Environment, Archetype Press, London, 2002
- John S. Mills, Raymond White, The Organic Chemistry of Museum Objects, Butterworth Heineman, London, 2nd ed., 1994
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000