Difference between revisions of "Magnesium carbonate"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
See also [[magnesium%20bicarbonate|magnesium bicarbonate]]). | See also [[magnesium%20bicarbonate|magnesium bicarbonate]]). | ||
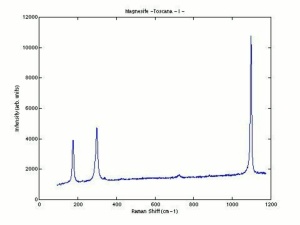
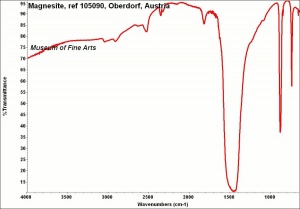
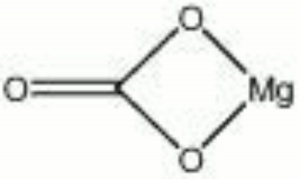
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Magnesiteitaly1.jpg~Raman|Magnesite, ref 105090, Oberdorf, Austria.jpg~FTIR|magnesium carbonate.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
magnesite; magnesia white; Pigment White 18; Magnesiumcarbonat (Deut.) | magnesite; magnesia white; Pigment White 18; Magnesiumcarbonat (Deut.) | ||
| − | + | == Risks == | |
| − | == | + | * Nontoxic. |
| + | * Ingestion has a laxative effect. | ||
| + | * Noncombustible. | ||
| + | * ThermoFisher: [https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=M263&productDescription=MAGNESIUM+CARBONATE+PURIF+3KG&vendorId=VN00033897&countryCode=US&language=en SDS] | ||
| + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
| − | Soluble in acids. Slightly soluble in water. Insoluble in ethanol. | + | * Soluble in acids. Slightly soluble in water. Insoluble in ethanol. |
| − | + | * Translucent, colorless, angular crystals; high birefringence under crossed polars; extinction is complete and straight. | |
| − | Translucent, colorless, angular crystals; high birefringence under crossed polars; extinction is complete and straight. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 27: | Line 30: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 350 (dec) | + | | 350 C (dec) |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 3.0 | + | | 3.0 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 38: | Line 41: | ||
| 1.508; 1.510; 1.700 | | 1.508; 1.510; 1.700 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
| Line 49: | Line 46: | ||
[[media:download_file_523.pdf|Characteristics of Common White Pigments]] | [[media:download_file_523.pdf|Characteristics of Common White Pigments]] | ||
| − | + | ==Resources and Citations== | |
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
* Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, ''Pigment Compendium'', Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004 | * Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, ''Pigment Compendium'', Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004 | ||
Latest revision as of 13:26, 16 October 2022
Description
A fluffy white powder used as an inert pigment and as an ingredient in inks, glass, ceramic glazes, and dentifrice. Magnesium carbonate has also been used as a sorbent powder for water-free (dry) cleaning of jewelry and doll hair. Aqueous solutions of magnesium carbonate are used for neutralization and alkalization of paper.
See also Magnesium bicarbonate).
Synonyms and Related Terms
magnesite; magnesia white; Pigment White 18; Magnesiumcarbonat (Deut.)
Risks
- Nontoxic.
- Ingestion has a laxative effect.
- Noncombustible.
- ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soluble in acids. Slightly soluble in water. Insoluble in ethanol.
- Translucent, colorless, angular crystals; high birefringence under crossed polars; extinction is complete and straight.
| Composition | MgCO3 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 546-93-0 |
| Melting Point | 350 C (dec) |
| Density | 3.0 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 84.3 |
| Refractive Index | 1.508; 1.510; 1.700 |
Comparisons
Characteristics of Common White Pigments
Resources and Citations
- Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, Pigment Compendium, Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- Tom Rowland, Noel Riley, A-Z Guide to Cleaning, Conserving and Repairing Antiques, Constable and Co., Ltd., London, 1981
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Book and Paper Group, Paper Conservation Catalog, AIC, 1984, 1989
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 5696