Difference between revisions of "Trioxane"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
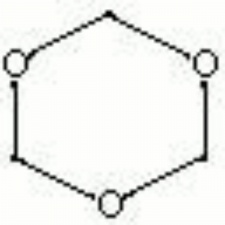
| − | White, crystalline solid with a [ | + | White, crystalline solid with a [[formaldehyde|formaldehyde]] odor. Trioxane is a trimer of anhydrous formaldehyde in a linked ring structure. It is used as a tanning agent and as a source for formaldehyde. Pellets of trioxane are used as a solid fuel in portable heating units. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|trioxane.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|trioxane.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Risks == |
| + | |||
| + | * Fire risk. Ignites readily. | ||
| + | * Burns with an odorless hot flame. | ||
| + | * Fisher Scientific: [https://fscimage.fishersci.com/msds/99076.htm MSDS] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
Soluble in water and polar organic solvents. Insoluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons. Decomposes with acids to produce formaldehyde. | Soluble in water and polar organic solvents. Insoluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons. Decomposes with acids to produce formaldehyde. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 28: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 62 | + | | 62 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 1.17 | + | | 1.17 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 31: | Line 37: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Boiling Point | ! scope="row"| Boiling Point | ||
| − | | 115 | + | | 115 C |
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 23 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 23 | ||
Latest revision as of 13:37, 16 June 2022
Description
White, crystalline solid with a Formaldehyde odor. Trioxane is a trimer of anhydrous formaldehyde in a linked ring structure. It is used as a tanning agent and as a source for formaldehyde. Pellets of trioxane are used as a solid fuel in portable heating units.
Synonyms and Related Terms
sym-trioxane; 1,3,5-trioxane; 1,3,5-trioxacyclohexane; metaformaldehyde; trioxymethylene; triformal
Risks
- Fire risk. Ignites readily.
- Burns with an odorless hot flame.
- Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in water and polar organic solvents. Insoluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons. Decomposes with acids to produce formaldehyde.
| Composition | (HCHO)3 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 110-88-3 |
| Melting Point | 62 C |
| Density | 1.17 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 90.08 |
| Boiling Point | 115 C |
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 23
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 9863