Difference between revisions of "Acacia"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:2003.314-SC70930.jpg|thumb|]] | + | [[File:2003.314-SC70930.jpg|thumb|Acacia wood bowl<br>MFA# 2003.314]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | + | [[File:72.4265-CR3662-d1.jpg|thumb|Egyptian stool<br>MFA# 74.4265]] | |
Evergreen trees and shrubs of the species of ''Acacia'' of the Leguminosae family. The trees are widely distributed through India, Hawaii, and Australia. Several commercial products are produced by these trees. [[Gum%20arabic|Gum arabic]] is produced from the sap and pods of ''Acacia arabic'' and ''Acacia senegal''. Kordofan gum comes from ''Acacia verek'' and is used in jellies, candies, and other food products. [[Cutch%20%28dye%29|Cutch]] is a brown or black dye obtained from ''Acacia catechu''. [[Wattle%20bark|Wattle bark]] produces a strongly astringent tannin from ''Acacia mimosa'' and ''Acacia mollisima'' trees. Strong, coarse bast fibers obtained from the ''Acacia leucophloea'' trees are used for ropes and nets. Some acacias are used for timber such as the ''Acacia melanoxylon'' (Australian blackwood), ''Acacia formosa'' (sabicu), Acacia seyal (shittah tree), and the ''Acacia koa'' (koa). The strong, elastic, hardwood is used for furniture, walking sticks, and tool handles. | Evergreen trees and shrubs of the species of ''Acacia'' of the Leguminosae family. The trees are widely distributed through India, Hawaii, and Australia. Several commercial products are produced by these trees. [[Gum%20arabic|Gum arabic]] is produced from the sap and pods of ''Acacia arabic'' and ''Acacia senegal''. Kordofan gum comes from ''Acacia verek'' and is used in jellies, candies, and other food products. [[Cutch%20%28dye%29|Cutch]] is a brown or black dye obtained from ''Acacia catechu''. [[Wattle%20bark|Wattle bark]] produces a strongly astringent tannin from ''Acacia mimosa'' and ''Acacia mollisima'' trees. Strong, coarse bast fibers obtained from the ''Acacia leucophloea'' trees are used for ropes and nets. Some acacias are used for timber such as the ''Acacia melanoxylon'' (Australian blackwood), ''Acacia formosa'' (sabicu), Acacia seyal (shittah tree), and the ''Acacia koa'' (koa). The strong, elastic, hardwood is used for furniture, walking sticks, and tool handles. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
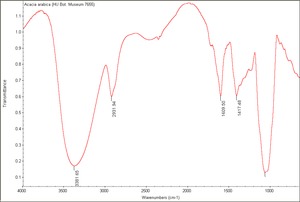
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|Acacia arabica (HU Bot. Museum 7655).TIF~FTIR (MFA)]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Acacia arabica (HU Bot. Museum 7655).TIF~FTIR (MFA)]]] | ||
| Line 11: | Line 9: | ||
Acacia melanoxylon (Australian blackwood); Borneo cutch; Acacia arabic; ''Acacia senegal; Acacia verek;'' Acacia catechu; Acacia mimosa; Acacia mollisima; Acacia leucophloea; Acacia koa; Acacia formosa (sabicu); Acacia seyal (shittim wood); Akacie (Dan.); Akazien (Deut.); acacia (Esp., Fr., It.. Ned.); Akacja (Pol.); acácia (Port.) | Acacia melanoxylon (Australian blackwood); Borneo cutch; Acacia arabic; ''Acacia senegal; Acacia verek;'' Acacia catechu; Acacia mimosa; Acacia mollisima; Acacia leucophloea; Acacia koa; Acacia formosa (sabicu); Acacia seyal (shittim wood); Akacie (Dan.); Akazien (Deut.); acacia (Esp., Fr., It.. Ned.); Akacja (Pol.); acácia (Port.) | ||
| − | == | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == |
Paper fiber type: hardwood. Using transmitted light microscopy, pulp is idenfied by small vessel elements with profuse alternate pitting that appears in horizontal rows. Perferations are simple . Appearance with [[Graff "C" stain]]: dark blue, varies with bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length, 0.8mm. 14μm wide. Common pulping method: [[kraft process|kraft]]. | Paper fiber type: hardwood. Using transmitted light microscopy, pulp is idenfied by small vessel elements with profuse alternate pitting that appears in horizontal rows. Perferations are simple . Appearance with [[Graff "C" stain]]: dark blue, varies with bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length, 0.8mm. 14μm wide. Common pulping method: [[kraft process|kraft]]. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 21: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
* F. H. Titmuss, ''Commercial Timbers of the World'', The Technical Press Ltd., London, 1965 | * F. H. Titmuss, ''Commercial Timbers of the World'', The Technical Press Ltd., London, 1965 | ||
| Line 37: | Line 35: | ||
* ''Fairchild's Dictionary of Textiles'', Phyllis G.Tortora, Robert S. Merkel (eds.), Fairchild Publications, New York City, 7th edition, 1996 | * ''Fairchild's Dictionary of Textiles'', Phyllis G.Tortora, Robert S. Merkel (eds.), Fairchild Publications, New York City, 7th edition, 1996 | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acacia (Dec. 30, 2005) |
* Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. ''Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers'' (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995. | * Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. ''Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers'' (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995. | ||
Latest revision as of 14:43, 18 April 2022
Description
Evergreen trees and shrubs of the species of Acacia of the Leguminosae family. The trees are widely distributed through India, Hawaii, and Australia. Several commercial products are produced by these trees. Gum arabic is produced from the sap and pods of Acacia arabic and Acacia senegal. Kordofan gum comes from Acacia verek and is used in jellies, candies, and other food products. Cutch is a brown or black dye obtained from Acacia catechu. Wattle bark produces a strongly astringent tannin from Acacia mimosa and Acacia mollisima trees. Strong, coarse bast fibers obtained from the Acacia leucophloea trees are used for ropes and nets. Some acacias are used for timber such as the Acacia melanoxylon (Australian blackwood), Acacia formosa (sabicu), Acacia seyal (shittah tree), and the Acacia koa (koa). The strong, elastic, hardwood is used for furniture, walking sticks, and tool handles.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Acacia melanoxylon (Australian blackwood); Borneo cutch; Acacia arabic; Acacia senegal; Acacia verek; Acacia catechu; Acacia mimosa; Acacia mollisima; Acacia leucophloea; Acacia koa; Acacia formosa (sabicu); Acacia seyal (shittim wood); Akacie (Dan.); Akazien (Deut.); acacia (Esp., Fr., It.. Ned.); Akacja (Pol.); acácia (Port.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
Paper fiber type: hardwood. Using transmitted light microscopy, pulp is idenfied by small vessel elements with profuse alternate pitting that appears in horizontal rows. Perferations are simple . Appearance with Graff "C" stain: dark blue, varies with bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length, 0.8mm. 14μm wide. Common pulping method: kraft.
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- F. H. Titmuss, Commercial Timbers of the World, The Technical Press Ltd., London, 1965
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 462
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Fairchild's Dictionary of Textiles, Phyllis G.Tortora, Robert S. Merkel (eds.), Fairchild Publications, New York City, 7th edition, 1996
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acacia (Dec. 30, 2005)
- Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995.
- Walter Rantanen. "Fiber ID Course." Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture.