Difference between revisions of "Copper acetate"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
Mallinckrodt Baker: [http://www.jtbaker.com/msds/englishhtml/c5808.htm MSDS] | Mallinckrodt Baker: [http://www.jtbaker.com/msds/englishhtml/c5808.htm MSDS] | ||
| − | == | + | == Sources Checked for Data in Record == |
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p.231 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p.231 | ||
Revision as of 13:20, 29 April 2016
Description
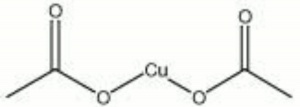
A dark green crystalline powder. Copper acetate is prepared by the reaction of Acetic acid with copper oxide. The green is unstable and can leave a black residue upon decomposition. Copper acetate is also used as a Pesticide, Fungicide, Catalyst, textile Dye and as a Pigment for paints, inks, and ceramics.
See also Copper acetate, basic.
Synonyms and Related Terms
cupric acetate; crystals of Venus, crystallized verdigris; verdet
Other Properties
Soluble in water, ethanol. Slightly soluble in ether, glycerol.
| Composition | Cu(C2H3O2)2-H2O |
|---|---|
| CAS | 142-71-2 |
| Melting Point | 115 |
| Density | 1.882 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 181.64 |
| Boiling Point | 240 (dec) |
Hazards and Safety
Toxic by ingestion. Contact causes irritation and burns.
Mallinckrodt Baker: MSDS
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p.231
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 2690