Difference between revisions of "Lead nitrate"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
White, translucent crystals that are produced by the reaction of [[nitric acid]] on [[lead]]. Lead nitrate is a strong oxidizing material. It is used as a [[mordant]] in dyeing and printing [[calico]] and for staining [[mother-of-pearl]]. Lead nitrate is also used as a sensitizer in photography and is used in engraving and lithographic processes. | White, translucent crystals that are produced by the reaction of [[nitric acid]] on [[lead]]. Lead nitrate is a strong oxidizing material. It is used as a [[mordant]] in dyeing and printing [[calico]] and for staining [[mother-of-pearl]]. Lead nitrate is also used as a sensitizer in photography and is used in engraving and lithographic processes. | ||
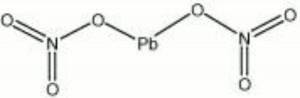
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|lead nitrate.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
lead (II) nitrate; lead dinitrate; plumbous nitrate; nitrato de plomo (II) (Esp.); | lead (II) nitrate; lead dinitrate; plumbous nitrate; nitrato de plomo (II) (Esp.); | ||
| − | [ | + | == Risks == |
| + | |||
| + | * Toxic by inhalation or ingestion. | ||
| + | * Skin contact may cause irritation or ulcers. | ||
| + | * Carcinogen, teratogen, suspected mutagen. | ||
| + | * ThermoFisher: [https://www.fishersci.com/msds?productName=AC193320100&productDescription=LEAD+%28II%29+NITRATE%2C+99.9999+10G&catNo=AC19332-0100&vendorId=VN00032119&storeId=10652 SDS] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== |
Soluble in water and ethanol. | Soluble in water and ethanol. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 27: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 290 (dec) | + | | 290 C (dec) |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 4.53 | + | | 4.53 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 31: | Line 36: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | ||
| Line 43: | Line 42: | ||
* ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 5434 | * ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 5434 | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lead_%28II%29_nitrate (Accessed Jan. 15, 2006) |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:21, 7 October 2022
Description
White, translucent crystals that are produced by the reaction of Nitric acid on Lead. Lead nitrate is a strong oxidizing material. It is used as a Mordant in dyeing and printing Calico and for staining Mother-of-pearl. Lead nitrate is also used as a sensitizer in photography and is used in engraving and lithographic processes.
Synonyms and Related Terms
lead (II) nitrate; lead dinitrate; plumbous nitrate; nitrato de plomo (II) (Esp.);
Risks
- Toxic by inhalation or ingestion.
- Skin contact may cause irritation or ulcers.
- Carcinogen, teratogen, suspected mutagen.
- ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in water and ethanol.
| Composition | Pb(NO3)2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 10099-74-8 |
| Melting Point | 290 C (dec) |
| Density | 4.53 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 331.2 |
Resources and Citations
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 5434
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lead_%28II%29_nitrate (Accessed Jan. 15, 2006)