Difference between revisions of "Whiting"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
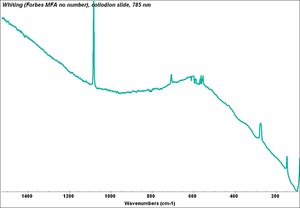
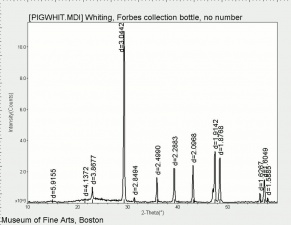
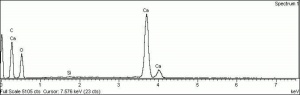
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|Whiting (Forbes MFA no number), collodion slide, 785 nm copy.tif~Raman (MFA)|PIGWHIT.jpg~XRD|fwhitingsem.jpg~SEM|fwhitingedsbw.jpg~EDS]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Whiting (Forbes MFA no number), collodion slide, 785 nm copy.tif~Raman (MFA)|PIGWHIT.jpg~XRD|fwhitingsem.jpg~SEM|fwhitingedsbw.jpg~EDS]]] | ||
| − | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | |
| − | == | ||
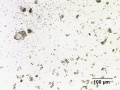
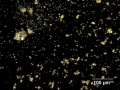
Small irregular shaped particles (0.1-10 microns); high birefringence with strong interference colors | Small irregular shaped particles (0.1-10 microns); high birefringence with strong interference colors | ||
| Line 30: | Line 29: | ||
[[media:download_file_526.pdf|Characteristics of Common White Pigments]] | [[media:download_file_526.pdf|Characteristics of Common White Pigments]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Additional Images == | == Additional Images == | ||
| Line 40: | Line 37: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | + | == Resources and Citations == | |
| − | == | ||
* Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, ''Pigment Compendium'', Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004 | * Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, ''Pigment Compendium'', Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004 | ||
Revision as of 14:05, 22 August 2020
Description
A fine powder of white Chalk (native Calcium carbonate). Whiting has been used as an inert pigment in paints, inks, and puttys and also as a flux in low temperature ceramic glazes. Synthetically prepared calcium carbonate, called precipitated chalk, is much whiter and finer than whiting.
Synonyms and Related Terms
chalk; whitening; Spanish white; limestone whiting; Paris white; English white; gilder's whiting; Pigment White 18; CI 77220
Physical and Chemical Properties
Small irregular shaped particles (0.1-10 microns); high birefringence with strong interference colors
Mmay fluoresce a medium purple color. Reacts with acids to evolve carbon dioxide.
| Density | 2.70 |
|---|---|
| Refractive Index | 1.486; 1.645 |
Comparisons
Properties of Common Abrasives
Characteristics of Common White Pigments
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, Pigment Compendium, Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 181
- Reed Kay, The Painter's Guide To Studio Methods and Materials, Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1983
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Paint in America, Robert Moss (ed.), John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1994 Comment: Ian Bristow "House Painting in Britain"
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000