Difference between revisions of "Chitin"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:Lobster.chitin.NOAA.jpg|thumb|Lobster | + | [[File:Lobster.chitin.NOAA.jpg|thumb|Lobster ''Homarus americanus'']] |
| − | |||
| − | ''Homarus americanus'']] | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| Line 14: | Line 12: | ||
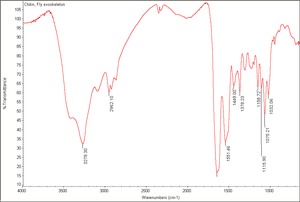
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|Chitin, Fly exoskeleton.TIF~FTIR (MFA)]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Chitin, Fly exoskeleton.TIF~FTIR (MFA)]]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Risks == |
| + | |||
| + | * ThermoFisher: [https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=AAJ6120622&productDescription=CHITIN+100G&vendorId=VN00024248&countryCode=US&language=en SDS] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ||
Soluble in concentrated mineral acids. Insoluble in common solvents. | Soluble in concentrated mineral acids. Insoluble in common solvents. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 29: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | ||
| Line 41: | Line 39: | ||
* ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 2105 | * ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 2105 | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chitin (accessed (Sept. 2, 2005) |
* Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | ||
Revision as of 14:41, 28 May 2022
Description
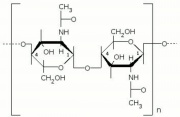
A tough, protective natural substance composed of a Nitrogen containing Polysaccharide. Chitin is the principal component in seashells as well as the exoskeletons of crabs, lobsters, insects, and beetles. It is also found in the cell walls of some fungi, Algae, and yeasts. Chitin is inelastic, thus growing arthropods must shed their exoskeletons periodically.
Synonyms and Related Terms
kitin (Dan.); Chitin (Deut.); quitina (Esp., Port.); chitine (Fr., Ned.); chitina (It.); chityna (Pol.)
Risks
- ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in concentrated mineral acids. Insoluble in common solvents.
| Composition | (C8H13NO5)n |
|---|---|
| CAS | 1398-61-4 |
Resources and Citations
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Walter C. McCrone, John Gustave Delly, The Particle Atlas, W. McCrone Associates, Chicago, IV, 1972
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 2105
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chitin (accessed (Sept. 2, 2005)
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000