Fungus
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Description
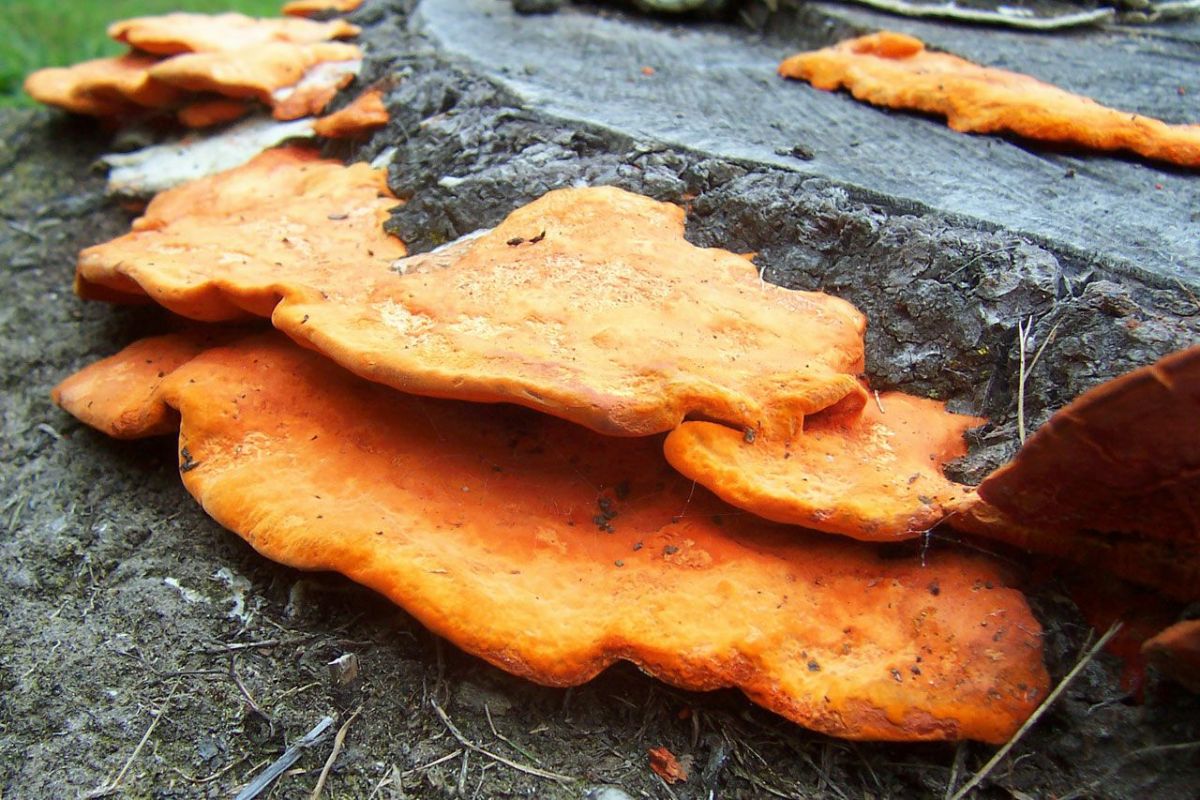
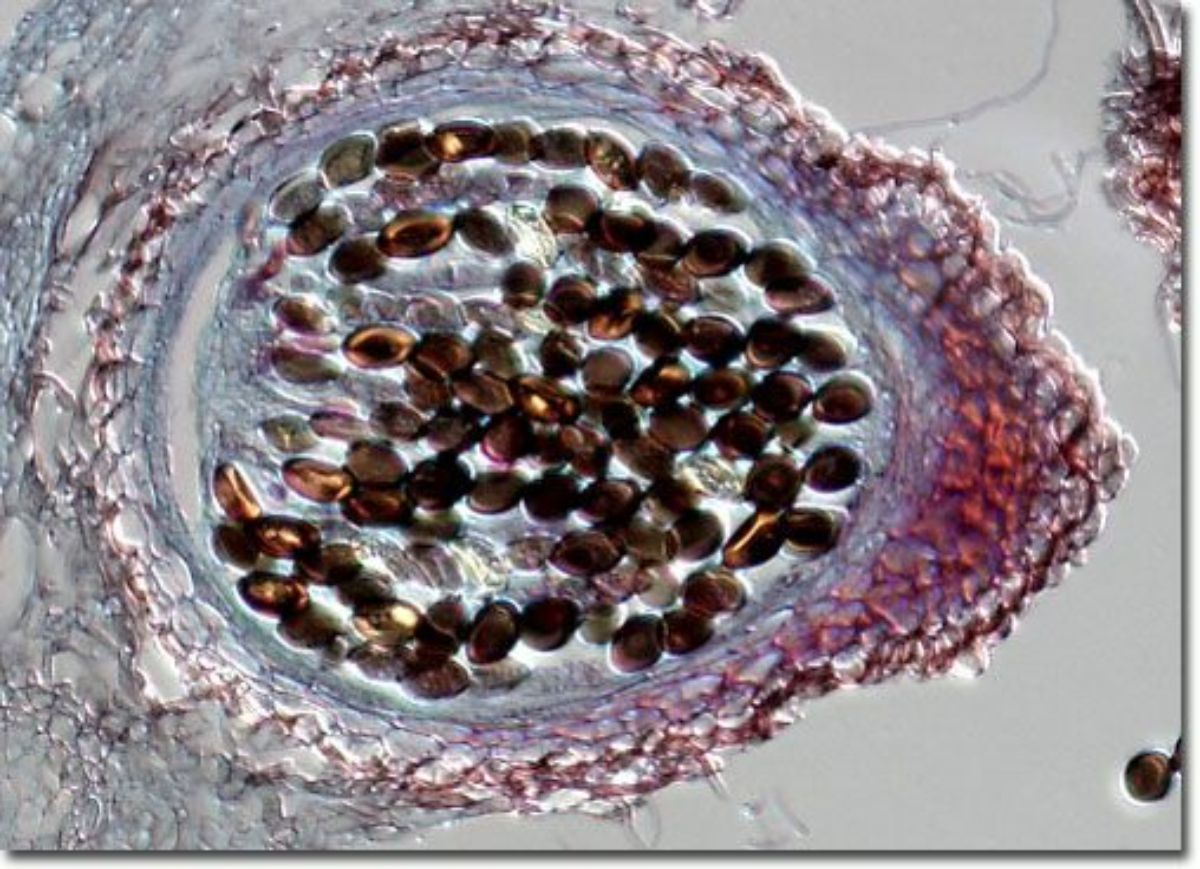
A group of simple plant-like organisms that do not produce chlorophyll. Examples of fungi include: mushrooms, yeasts, Molds, Smuts, and mildew. Fungi are parasitic. They will infiltrate and consume wood, paper, or other growth media. They need warmth, oxygen, food, and relatively high humidities for optimum growth. Fungi are spread by airborne spores emitted from fruiting bodies.
Synonyms and Related Terms
fungi (plural); mold; mildew; smut; yeast; mushroom; fruiting bodies; svampe (Dan.); Pilze (Deut.); fungi (Esp., It.); champignon (Fr.); mycètes (Fr.); funghi (It.); miceti (It.); schimmels (Ned.); zwammen (Ned.); sopper (Nor.); grzyby (Pol.); fungos (Port.); svampar (Sven.);
Resources and Citations
- E.McCrady, "Mold: The Whole Picture, Pt.1" The Abbey Newsletter, Vol. 23 (4), 1999. Link
- Mary-Lou Florian, Fungal Facts: solving fungal problems in heritage collections, Archetype, London, 2002
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fungus (Accessed Nov. 2, 2005)
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Walter C. McCrone, John Gustave Delly, The Particle Atlas, W. McCrone Associates, Chicago, IV, 1972
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Hermann Kuhn, Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities, Butterworths, London, 1986
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 930
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- AMOL reCollections Glossary - http://amol.org.au/recollections/7/f/htm
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998