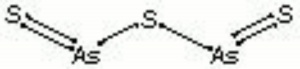Difference between revisions of "Arsenic trisulfide"
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
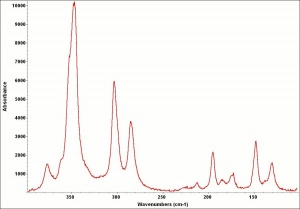
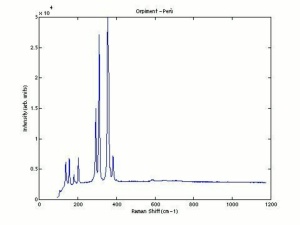
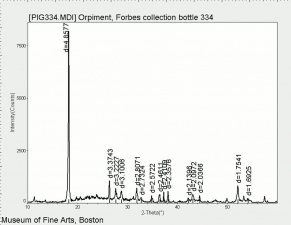
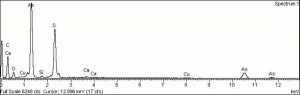
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|OrpimentUCL.jpg~Raman|Orpimentitaly1.jpg~Raman|PIG334.jpg~XRD|f334sem.jpg~SEM|f334edsbw.jpg~EDS|arsenic trisulfide.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|OrpimentUCL.jpg~Raman|Orpimentitaly1.jpg~Raman|PIG334.jpg~XRD|f334sem.jpg~SEM|f334edsbw.jpg~EDS|arsenic trisulfide.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Risks == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Highly toxic by ingestion and inhalation. | ||
| + | * Skin contact causes irritation. | ||
| + | * Carcinogen and mutagen. | ||
| + | * Fisher Scientific: [https://fscimage.fishersci.com/msds/84980.htm MSDS] | ||
==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ||
| Line 40: | Line 47: | ||
| 707 C | | 707 C | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Resources and Citations== | ==Resources and Citations== | ||
Revision as of 10:22, 30 April 2022
Description
A bright yellow, crystalline powder that occurs naturally as the mineral Orpiment. Orpiment is often found with lead and silver ores along with Realgar (arsenic disulfide). It was once widely used as a pigment because of its bright rich color. However, it is extremely toxic which has limited its use and availability. Arsenic trisulfide was also used to dehair and tan leathers, to kill rodents, and to print calico textiles. It is still used in fireworks and in the manufacture of infrared transmitting glass.
Synonyms and Related Terms
arsenic (III) sulfide; Pigment Yellow 39; CI 77085, 77086; orpiment (mineral); arsenic sulphide (Br.); Operment (Deut.); Rauschgelb (Deut.); Konigsgelb (Deut.); jaune royal (Fr.); trisulfure d'arsenic (Fr.); oropimente (Esp.); orpimento (It.); trisolfuro d'arsenico (It.); kio (Jap.); sekio (Jap.); ouropigmento (Port.); yellow arsenic sulfide; king's yellow; arsenic yellow; jaune royal; king's gold; arsenous sulfide; arsenic tersulfide; arsenious sulfide; auripigment
Risks
- Highly toxic by ingestion and inhalation.
- Skin contact causes irritation.
- Carcinogen and mutagen.
- Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soluble in nitric acid and alkali sulfide solutions. Insoluble in water and hydrochloric acid.
- Small, often elongated particles (4-20 microns);
- Strong yellow particles with high birefringence and straight extinction
| Composition | As2S3 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 1303-33-9 |
| Melting Point | 300 C |
| Density | 3.43 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 246.04 |
| Refractive Index | 2.40; 2.81; 3.02 |
| Boiling Point | 707 C |
Resources and Citations
- Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, Pigment Compendium, Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arsenic_trisulfide (accessed Aug. 30, 2005)
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 69
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 846
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985