Difference between revisions of "Styrene-butadiene rubber"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | butadiene styrene; Buna-S; SBR; butadieno-estireno (Esp.); butadiène-styrène (Fr.); butadieno-estireno (Port.) | + | butadiene styrene; Buna-S; SBR rubber; butadieno-estireno (Esp.); butadiène-styrène (Fr.); butadieno-estireno (Port.) |
== Applications == | == Applications == | ||
Latest revision as of 11:28, 18 October 2022
Description
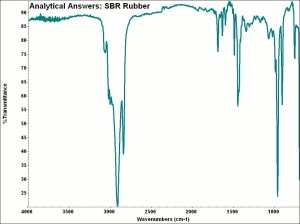
An elastomer made by copolymerizing Butadiene with Styrene. Styrene-butadiene rubber is commonly called Buna-S and SBR. Large amounts of the copolymer were first commercially produced in the 1930s as a synthetic replacement for natural rubber. Currently, styrene-butadiene is the most widely used synthetic rubber. SBR has good water and heat resistance but poor Oil, Solvent, and Oxidation resistance. It also has a tendency to crawl. SBR is used for tires, footwear, adhesives, coatings, and carpet backing.
Synonyms and Related Terms
butadiene styrene; Buna-S; SBR rubber; butadieno-estireno (Esp.); butadiène-styrène (Fr.); butadieno-estireno (Port.)
Applications
Risks
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 629
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Pam Hatchfield, Pollutants in the Museum Environment, Archetype Press, London, 2002
- M.Kaufman, The First Century of Plastics, The Plastics and Rubber Institute, London, 1963
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000
- Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', Engineered Plastics, ASM International, 1988