Difference between revisions of "Henna"
(username removed) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A reddish-orange dyestuff that comes from the leaves of small evergreen trees, ''Lawsonia inermis'' or ''Lawsonia alba'', native to the Middle East, northern Africa and Asia. Henna was used by the ancient Egyptians and Asians for dyeing [ | + | A reddish-orange dyestuff that comes from the leaves of small evergreen trees, ''Lawsonia inermis'' or ''Lawsonia alba'', native to the Middle East, northern Africa and Asia. Henna was used by the ancient Egyptians and Asians for dyeing [[hair]], nails, skin, [[leather]], [[wool]], and [[silk]]. Henna-dyed cloth was sometimes used for mummy wrappings. The principle colorant in henna is lawsone and it also contains [[juglone]], [[luteolin]], and several tannins. Lawsone is a red [[substantive dye]] that is very effective on the protein [[keratin]]. Henna has also been used as a [[fungicide]]. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
Revision as of 10:55, 16 January 2014
Description
A reddish-orange dyestuff that comes from the leaves of small evergreen trees, Lawsonia inermis or Lawsonia alba, native to the Middle East, northern Africa and Asia. Henna was used by the ancient Egyptians and Asians for dyeing Hair, nails, skin, Leather, Wool, and Silk. Henna-dyed cloth was sometimes used for mummy wrappings. The principle colorant in henna is lawsone and it also contains Juglone, Luteolin, and several tannins. Lawsone is a red Substantive dye that is very effective on the protein Keratin. Henna has also been used as a Fungicide.
Synonyms and Related Terms
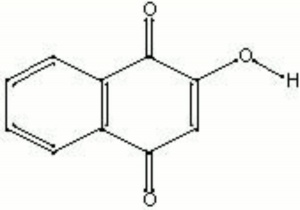
2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione; Natural Orange 6; CI 75480; henna (Esp.); henné (Fr.); hena (Port.); English privet; flowers of paradise; lawsone; 2-hydroxy-p-naphthoquinone; 2-hydroxynaphthoquinone; hennis; hana; alkanna; gopherwood; mignonette; mehandi; mendi
Other Properties
Lawsone is soluble in water, ether.
| Composition | C10H6O3 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 83-72-7 |
| Melting Point | 192 (dec) |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 174.0402 |
Hazards and Safety
Contact, inhalation or ingestion may cause irritation.
Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Additional Information
° J.Hofenk-de Graaf, Natural Dyestuffs: Origin, Chemical Constitution, Identification, Central Research Laboratory for Objects of Art and Science, Amsterdam, September 1969.
Authority
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 283
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Myrtales" Encyclopædia Britannica [Accessed May 6, 2002]. Lawsonia inermis
- Palmy Weigle, Ancient Dyes for Modern Weavers, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York, 1974
- John and Margaret Cannon, Dye Plants and Dyeing, Herbert Press, London, 1994
- A.Lucas, J.R.Harris, Ancient Egyptian Materials and Industries, Edward Arnold Publishers Ltd., London, 4th edition, 1962
- F. Crace-Calvert, Dyeing and Calico Printing, Palmer & Howe, London, 1876
- Judith Hofenk-de Graaff, Natural Dyestuffs: Origin, Chemical Constitution, Identification, Central Research Laboratory for Objects of Art and Science, Amsterdam, 1969
- J. Thornton, 'The Use of Dyes and Colored Varnishes in Wood Polychromy', Painted Wood: History and Conservation, The Getty Conservation Insitute, Los Angeles, 1998
- Helmut Schweppe, Schweppe color collection index and information book
- Colour Index International online at www.colour-index.org