Difference between revisions of "Hardwood"
JMcGlinchey (talk | contribs) |
JMcGlinchey (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Redoak vessels 10x.jpg|Red oak paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | File:Redoak vessels 10x.jpg|Red oak paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| + | Sycamore 40x.jpg|American sycamore paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| + | Redgum 10x.jpg|Red gum paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| + | Yellowpoplar 40x.jpg|Yellow poplar paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| + | Blackcherry 10x.jpg|Black cherry paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| + | Yellowbirch 10x.jpg|Yellow birch paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| + | Aspen 40x2.jpg|Aspen paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
| + | Ash 10x.jpg|Ash paper pulp stained with Graff "C" stain | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 07:57, 17 July 2015
Description
One of two common classifications for trees, hardwood (angiosperm) and Softwood (gymnosperm). Hardwoods are broad-leaved deciduous trees that vary widely in color and grain pattern. Examples of hardwood trees are: ash, Beech, Birch, cherry, Mahogany, Maple, Oak, Poplar, and Walnut. Hardwood trees are found in temperate and tropical climate zones. Most of the wood used for cabinetry, furniture and flooring is obtained from hardwood trees. Only a small amount of hardwood is used for paper pulp. The term hardwood is somewhat confusing since some deciduous trees, such as basswood, have timber that is softer than some coniferous trees, such as yellow pine.
Synonyms and Related Terms
bois dur (Fr.); koboku (Jap.); frondosa (Esp.) ;folhosa (Port.); latifoglia (It.); nonconiferous wood; angiosperm; deciduous
Other Properties
Contain open-ended pores or vessels.
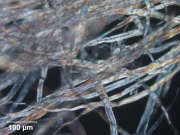
Paper fiber type: hardwood. Using transmitted light microscopy, pulp is identified by the presence of vessel elements with species specific morphological characteristics such as pitting, type of perforation, size, shape, etc. Fibers are short with thin walls. Appearance with Graff "C" stain: varies with pulping process and bleaching; Kraft=dark blue, sulfite=light blue. Average dimensions of fibers: length, 0.9 mm; width, 15-25 μm. Common pulping method: kraft dominates, but several species can be pulped using the Sulfite process.
Additional Images
Authority
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Walter C. McCrone, John Gustave Delly, The Particle Atlas, W. McCrone Associates, Chicago, IV, 1972
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- The Dictionary of Paper, American Paper Institute, New York, Fourth Edition, 1980
- Pam Hatchfield, Pollutants in the Museum Environment, Archetype Press, London, 2002
- Website address 1 Comment: Museum of Japanese Traditional Art Crafts at http://www.nihon-kogeikai.com/ (Jap. term)