Difference between revisions of "Nitroglycerin"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(username removed) |
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
Compound can be desensitized by cooling to 5-10 C but then should never be warmed as thawing is extremely hazardous. | Compound can be desensitized by cooling to 5-10 C but then should never be warmed as thawing is extremely hazardous. | ||
| − | == | + | == Sources Checked for Data in Record == |
* Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000 | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000 | ||
Revision as of 13:12, 1 May 2016
Description
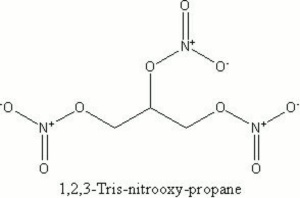
A heavy, poisonous, oily compound that is unstable and can readily explode. Nitroglycerin was discovered by Ascanio Sobrero in 1847. A safe manufacturing process was developed by Alfred Nobel in the 1860s. Nitroglycerin is prepared by the nitration of glycerol. It is used to make dynamite.
Synonyms and Related Terms
nitroglycerine; glyceryl trinitrate; trinitroglycerin; Swedish blasting oil; nitroglycerin (Dan., Sven.); Glycerintrinitrat (Deut.); nitroglicerina (Esp., It., Port.); nitroglycérine (Fr.); trinitrine (Fr.); Nitroglycerine (Ned.); nitrogliceryna (Pol.); triazotan glicerol (Pol.); (Port.)
| Composition | C3H5N3O9 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 55-63-0 |
| Melting Point | 13.2 |
| Density | 1.13 |
| Molecular Weight | 227.0872 |
| Boiling Point | 50-60 (decomposes) |
Hazards and Safety
Compound can be desensitized by cooling to 5-10 C but then should never be warmed as thawing is extremely hazardous.
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nitroglycerin (Accessed Oct. 18, 2005)