Difference between revisions of "Styrene"
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
m (Text replace - "\[http:\/\/cameo\.mfa\.org\/materials\/fullrecord\.asp\?name=([^\s]+)\s(.*)\]" to "$2") |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A colorless, oily liquid, Styrene was first isolated from [ | + | A colorless, oily liquid, Styrene was first isolated from [[storax|storax]] in 1831 by Bonastre. It readily self-polymerizes with heat, light or catalyst. The polymerization step is exothermic. Styrene is primarily used as an ingredient in polymers such as [[polystyrene|polystyrene]], [[styrene-butadiene%20rubber|styrene-butadiene rubber]] (SBR) and [[acrylonitrile%20butadiene%20styrene%20resin|acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene]] (ABS). It has also been used as a solvent in paints, lacquers and plastics. For example, it is used as a polymerizing solvent in [[Bio-Plastic%C2%AE|Bio-Plastic®]] embedding resin. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
Revision as of 11:35, 10 May 2016
Description
A colorless, oily liquid, Styrene was first isolated from Storax in 1831 by Bonastre. It readily self-polymerizes with heat, light or catalyst. The polymerization step is exothermic. Styrene is primarily used as an ingredient in polymers such as Polystyrene, Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS). It has also been used as a solvent in paints, lacquers and plastics. For example, it is used as a polymerizing solvent in Bio-Plastic® embedding resin.
Synonyms and Related Terms
vinylbenzene; cinnamene; phenylethylene; phenyl ethylene; ethenylbenzene; styrol; styrolene; cinnamol
Other Properties
Soluble in ethanol, ether. Insoluble in water.
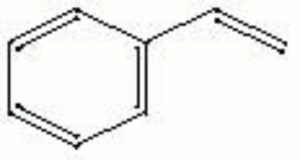
| Composition | C6H5CH=CH2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 100-42-5 |
| Melting Point | -30.63 |
| Density | 0.9045 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt.=104.15 |
| Refractive Index | 1.545 |
| Boiling Point | 145.2 |
Hazards and Safety
Flammable. Flash point = 31 C (88 F)
Ingestion, inhalation and contact cause irritation. Carcinogenic.
Mallinckrodt Baker: MSDS
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 9028
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 627
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- ASTM, "Standard Terminology Relating to Paint, Varnish, Lacquer and Related Products", Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Section 6, Paints, Related Coatings and Aromatics, ASTM, D16, 7-Jan, Jul-96
- Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979 Comment: flash point = 32C
- M.Kaufman, The First Century of Plastics, The Plastics and Rubber Institute, London, 1963
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: ref. index=1.545