Difference between revisions of "Teflon"
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
m (Text replace - "\[http:\/\/cameo\.mfa\.org\/materials\/fullrecord\.asp\?name=([^\s]+)\s(.*)\]" to "$2") |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | [DuPont] A registered trademark for a solid white polymer that is resistant to almost all chemicals. [ | + | [DuPont] A registered trademark for a solid white polymer that is resistant to almost all chemicals. [[Polytetrafluoroethylene|Polytetrafluoroethylene]] was accidentally discovered in 1938 by Roy Plunkett at DuPont during an attempt to synthesize tetrafluoroethylene. The new polymer was resistant to heat, chemical, light, and adhesion. It was marketed as Teflon by DuPont in 1943. Teflon is a soft, opaque material that is unaffected by acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. It is widely used for containers in chemical plants, for rockets, bearings, gaskets, and for frying pan coatings. Teflon is used for stain-resistant, water-repellent coatings on textiles. It can also be prepared as ribbonlike fibers, which are woven, knitted, felted or braided. Additionally, [[GORE-TEX|GORE-TEX]] is prepared from a microporous Teflon film laminated on a polyester fabric. |
See also fluorinated ethylene propylene. | See also fluorinated ethylene propylene. | ||
Revision as of 11:45, 10 May 2016
Description
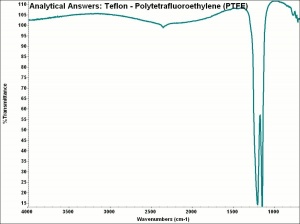
[DuPont] A registered trademark for a solid white polymer that is resistant to almost all chemicals. Polytetrafluoroethylene was accidentally discovered in 1938 by Roy Plunkett at DuPont during an attempt to synthesize tetrafluoroethylene. The new polymer was resistant to heat, chemical, light, and adhesion. It was marketed as Teflon by DuPont in 1943. Teflon is a soft, opaque material that is unaffected by acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. It is widely used for containers in chemical plants, for rockets, bearings, gaskets, and for frying pan coatings. Teflon is used for stain-resistant, water-repellent coatings on textiles. It can also be prepared as ribbonlike fibers, which are woven, knitted, felted or braided. Additionally, GORE-TEX is prepared from a microporous Teflon film laminated on a polyester fabric.
See also fluorinated ethylene propylene.
Synonyms and Related Terms
PTFE; polytetrafluoroethylene; Polytetrafluorethylen (Deut.); politetrafluoretileno (Esp.); polyttrafluorthylne (Fr.); Teflon (Port.)
Examples: GORE-TEX [W.R.Gore]; Teflon TFE [DuPont]; Rulon [Saint-Gobain]; Algoflon [Solvay]; Fluorosint [Quadrant];
Other Properties
Highly resistant to acids, alkalis and solvents. Tenacity = 0.5-1.4 g/denier; Elongation = 15-32 %; Moisture regain = 0%; 1 mil films: 0.1 g/m2d
| Melting Point | 300 (dec) |
|---|---|
| Density | 2.1-2.3 |
Hazards and Safety
Does not burn in flame but evaporates above 215C and evolves HF.
Additional Information
DuPont: Teflon Website G.Cook, Handbook of Textile Fibres:II. Man-made Fibres, 5th edition, Merrow Publishing Co., Durham, England, 1984. p.509.
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- G.S.Brady, G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971
- Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990
- Marjory L. Joseph, Marjory L. Joseph, Introductory Textile Science, Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Fort Worth, TX, 1986
- Identification of Textile Materials, The Textile Institute, Manchester, England, 1985
- J.Gordon Cook, J.Gordon Cook, Handbook of Textile Fibres:II Man-made Fibres, Merrow Publishing Co. , Durham, England
- Theodore J. Reinhart, Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', Engineered Plastics, ASM International, 1988