Difference between revisions of "Desert Poplar (Populus euphratica) LC"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | Desert Poplar (''Populus euphratica'')is a medium-sized deciduous tree. It may grow to a height of about 15 m and a girth of 2.5 m (8.2 ft) where conditions are favourable. The stem is typically bent and forked; old stems have thick, rough, olive-green bark. While the sapwood is white, the heartwood is red, darkening to almost black at the center. The roots spread widely but not deeply. The leaves are highly variable in shape. The species has a very wide range, occurring naturally from North Africa, across the Middle East and Central Asia to western China. Its forests have largely disappeared or become fragmented over much of its natural range. | + | Desert Poplar, 胡杨, (''Populus euphratica'')is a medium-sized deciduous tree. It may grow to a height of about 15 m and a girth of 2.5 m (8.2 ft) where conditions are favourable. The stem is typically bent and forked; old stems have thick, rough, olive-green bark. While the sapwood is white, the heartwood is red, darkening to almost black at the center. The roots spread widely but not deeply. The leaves are highly variable in shape. The species has a very wide range, occurring naturally from North Africa, across the Middle East and Central Asia to western China. Its forests have largely disappeared or become fragmented over much of its natural range. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
== Historical importance == | == Historical importance == | ||
Revision as of 09:57, 1 September 2017
Description
Desert Poplar, 胡杨, (Populus euphratica)is a medium-sized deciduous tree. It may grow to a height of about 15 m and a girth of 2.5 m (8.2 ft) where conditions are favourable. The stem is typically bent and forked; old stems have thick, rough, olive-green bark. While the sapwood is white, the heartwood is red, darkening to almost black at the center. The roots spread widely but not deeply. The leaves are highly variable in shape. The species has a very wide range, occurring naturally from North Africa, across the Middle East and Central Asia to western China. Its forests have largely disappeared or become fragmented over much of its natural range.
Historical importance
The species is used in agroforestry to provide leaves as fodder for livestock, timber and, potentially, fiber for making paper. It is also used in afforestation programs on saline soils in desert regions, and to create windbreaks and check erosion.
Summary of results
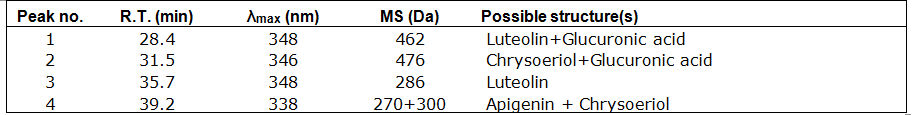
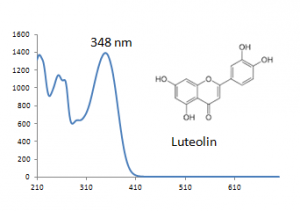
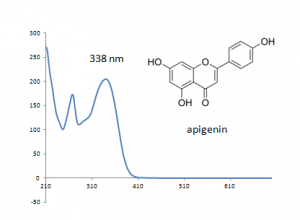
Multiple flavonoids, luteolin, apigenin, chrysoeriol and their glycosides were identified from desert poplar dyed wool samples.
Comments: • Acid hydrolysis showed significant amounts of flavone glycosides, probably luteolin and chrysoeriol glucuronides, which are known to be resistant to acid hydrolysis, as well as luteolin and chrysoeriol. • Other methylated derivatives of luteolin may also be present.
Analytical instrumentation and procedures
Chromatograms
Sample information
Identified compounds
| Compound | RT (min.) | MW | UV/vis | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Luteolin | 35.7 | 286 | 348 | |
| Apigenin | 39.2 | 270 | 338 |
References
[1] [2] [3]