Difference between revisions of "Cadmium yellow"
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
cadmium sulfide; Pigment Yellow 37; CI 77191; Kadmiumgelb (Deut.); jaune de cadmium (Fr.); cadmium sulphide (Br.); giallo di cadmio (It.); amarillo de cadmio (Esp.); kitrino toy kadmioy (Gr.); cadmiumgeel (Ned.); amarelo de cádmio (Port.); cadmium lithopone; cadmopone; Aurora yellow; daffodil; radiant yellow; cadmia; Orient yellow; jaune brilliant; Cadmolith | cadmium sulfide; Pigment Yellow 37; CI 77191; Kadmiumgelb (Deut.); jaune de cadmium (Fr.); cadmium sulphide (Br.); giallo di cadmio (It.); amarillo de cadmio (Esp.); kitrino toy kadmioy (Gr.); cadmiumgeel (Ned.); amarelo de cádmio (Port.); cadmium lithopone; cadmopone; Aurora yellow; daffodil; radiant yellow; cadmia; Orient yellow; jaune brilliant; Cadmolith | ||
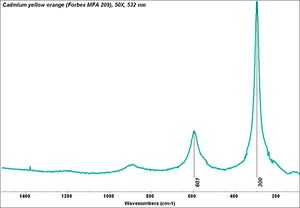
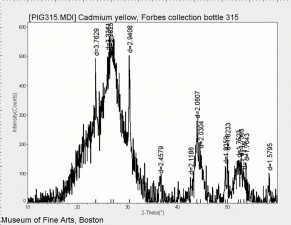
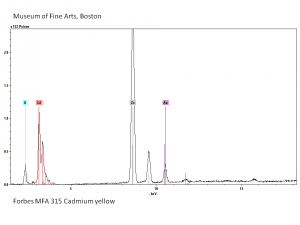
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|PIG315.jpg~XRD|f315sem.jpg~SEM|f315edsbw.jpg~EDS|Slide25 FC315.PNG~XRF]]] | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Cadmium yellow orange (Forbes MFA 209), 50X, 532 nm copy.jpg~Raman (MFA)|PIG315.jpg~XRD|f315sem.jpg~SEM|f315edsbw.jpg~EDS|Slide25 FC315.PNG~XRF]]] |
== Other Properties == | == Other Properties == | ||
Revision as of 11:04, 12 December 2019
Description
A permanent, yellow pigment composed of Cadmium sulfide. Cadmium yellows were synthetically prepared in Germany by Friedrich Strohmeyer in 1817. The bright yellow pigments slowly began to be used as artist paints in the mid 1840s, gaining in popularity in the early 20th century. Variations in particle size and chemical composition produce as range of colors from light yellow to orange. In the 1920s, the cadmium pigments were co-precipitated with Barium sulfate to form the cheaper cadmium lithopone (cadmopone) pigments. Cadmium sulfide also occurs in minor amounts in the mineral greenockite.
Synonyms and Related Terms
cadmium sulfide; Pigment Yellow 37; CI 77191; Kadmiumgelb (Deut.); jaune de cadmium (Fr.); cadmium sulphide (Br.); giallo di cadmio (It.); amarillo de cadmio (Esp.); kitrino toy kadmioy (Gr.); cadmiumgeel (Ned.); amarelo de cádmio (Port.); cadmium lithopone; cadmopone; Aurora yellow; daffodil; radiant yellow; cadmia; Orient yellow; jaune brilliant; Cadmolith
Other Properties
Cubic or hexagonal crystals. Soluble in concentrated mineral acids with the evolution of H2S. Insoluble in water. May fluoresce red.
The tiny yellow particles (about 1 micrometer) have a high refractive index.
| Composition | CdS |
|---|---|
| Density | 4.35 |
| Molecular Weight | 144.48 |
| Refractive Index | e=2.506, w=2.529 |
Hazards and Safety
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation. Carcinogen.
Additional Information
° I. Fiedler, M. Bayard, "Cadmium yellows, oranges and reds", Artists Pigments, Volume 1, R. Feller (ed.), Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1986.
Additional Images
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, Pigment Compendium, Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: density = 4.35 and ref. index = 2.35-2.48
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Website address 1 Comment: Pigments Through the Ages: http://webexhibits.org/pigments/indiv/technical/cdyellow.html - e=2.506, w=2.529
- Thomas B. Brill, Light Its Interaction with Art and Antiquities, Plenum Press, New York City, 1980
- The Dictionary of Art, Grove's Dictionaries Inc., New York, 1996 Comment: 'Pigments'
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000