Difference between revisions of "Nylon 6"
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
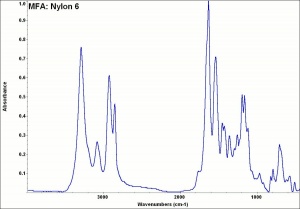
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|MFA- Nylon 6.jpg~FTIR]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|MFA- Nylon 6.jpg~FTIR]]] | ||
| + | == Personal Risks == | ||
| − | == | + | Stratasys: [http://www.hoehnplastics.com/pdf/sds-104-polyamide-6-nylon-6.pdf SDS] |
| + | |||
| + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
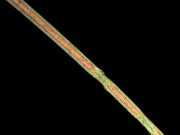
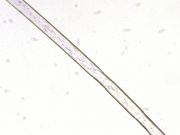
Resistant to alkalis and most organic solvents. Degraded by concentrated acids and phenol. Burns with yellow-orange flame and blue smoke; smells of burnt horn. Fiber is smooth. Cross section is circular. Tenacity = 3.8-8.3 g/denier (dry); 3.5-7.1 (wet); Elongation = 16-50% (dry); 19-55 % (wet); Moisture regain = 3.5-5.0% (dry) | Resistant to alkalis and most organic solvents. Degraded by concentrated acids and phenol. Burns with yellow-orange flame and blue smoke; smells of burnt horn. Fiber is smooth. Cross section is circular. Tenacity = 3.8-8.3 g/denier (dry); 3.5-7.1 (wet); Elongation = 16-50% (dry); 19-55 % (wet); Moisture regain = 3.5-5.0% (dry) | ||
| Line 31: | Line 34: | ||
| 1.14 | | 1.14 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
Revision as of 12:11, 26 July 2020
Description
Nylon 6 is made by polymerizing Caprolactam under pressure. Nylon 6 was first sold as Perlon L in 1939 by I.G.Farbenindustrie. It was produced during W.W.II for parachutes. Nylon 6 is very similar to Nylon 6,6 except that it has a greater affinity for dyes and has a lower melting point. Its Thermoplastic fibers are strong, tough, elastic and have high gloss. They are extruded through a spinneret with a circular cross section. Nylon monofilaments are used for brushes, surgical sutures, tennis strings, and fishing lines. Nylon 6 is also used for heat-seal films because it has low water vapor transmission rates. Cellular nylon foam is made from nylon 6 for lightweight buoys and flotation products.
See also Nylon fiber.
Synonyms and Related Terms
polycaprolactam; Perlon® [I.G.Farbenindustrie]; Caprolan® [Honeywell]; Kapron; Silon; Dederon; Danamid; Nivion; Enka®; Hydrofil [Honeywell]; Powersilk [BASF]; Dorlon (later called Bayer-Perlon) [Bayer]; Bobingen (later called Hoescht-Perlon) [Hoescht]
Personal Risks
Stratasys: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Resistant to alkalis and most organic solvents. Degraded by concentrated acids and phenol. Burns with yellow-orange flame and blue smoke; smells of burnt horn. Fiber is smooth. Cross section is circular. Tenacity = 3.8-8.3 g/denier (dry); 3.5-7.1 (wet); Elongation = 16-50% (dry); 19-55 % (wet); Moisture regain = 3.5-5.0% (dry)
| Composition | (C6H11NO)n |
|---|---|
| CAS | 25038-54-4 |
| Melting Point | 210-217 |
| Density | 1.14 |
Comparisons
Properties of Synthetic Fibers
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Marjory L. Joseph, Introductory Textile Science, Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Fort Worth, TX, 1986, p. 135.
- J.Gordon Cook, Handbook of Textile Fibres:II Man-made Fibres, Merrow Publishing Co., Durham, England, 1984, p.261.
- F. Kidd, Brushmaking Materials, Bristish Brush Manufacturers, London, 1957
- Meredith Montague, contributed information, 1998