Nylon fiber
Description
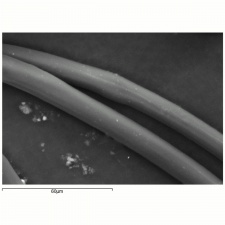
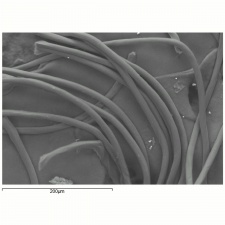
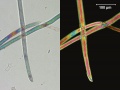
A generic name for any manufactured fiber in which the fiber-forming substance is any long chain synthetic Polyamide having recurring amide groups (-NH-CO) as an integral part of the polymer chain (Federal Trade Commission definition). Nylon 6,6 was first made in the early 1930s by W. H.Carothers as a textile fiber called fiber #66; the name nylon was coined in 1938 by DuPont. By 1939, nylon 6,6 and nylon 6 were being commercially produced in the US and Germany, respectively. Nylon 6,6 and nylon 6 are still the most common nylons used in fibers. All nylons are strong, tough, elastic and have high gloss. They are extruded through a spinneret and have a circular cross section. Nylon monofilaments are used for brushes, surgical sutures, tennis strings and fishing lines. Titanium dioxide may be added to the surface of nylon fibers to reduce luster. Nylon fibers are used for clothing, undergarments, linings, carpets, tire cords, conveyor belts, parachutes, hosiery and brushes. Nylon fibers have excellent dyeability and are twice as durable as Cotton.
See also Nylon resin and Qiana.
For Nylon fiber identification; see http://cameo.mfa.org/wiki/Category:FRIL:_Nylon
Synonyms and Related Terms
nylon fibre; fiber #66; nylon 6,6; nylon 6; nylon PACM-12; nylon 7; nylon 12; nylon 6T; nylon 6,10; nylon 4,6; Nylon; Enkalon; Perlon® [Germany]; Antron; Durasoft; Supplex; Celon; Dederon; Ultron; Tecron; Rilsan®; fibra de nailon, nilón(Esp.)
Risks
- Potential degradation products are carbon monoxide and cyanogen.
- Degraded by sunlight.
- Flame resistant.
- In a continuous flame, nylon melts first, then ignites and burns rapidly. It smells like burnt plastic.
- Resistant to insects and microorganisms.
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Resistant to alkalis and insoluble in most organic solvents.
- Soluble in hot phenols, cresols and mineral acids.
- Moisture regain = 4.2-5.0%.
- Melting Point = 250 C
- Density = 1.14 g/ml
- Refractive Index = 1.53
Comparisons
Properties of Synthetic Fibers
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- M. Joseph, Introductory Textile Science, Holt Reinhold & Winston, Fort Worth, 1986, p. 135.
- G.Cook, Handbook of Textile Fibres:II. Man-made Fibres, 5th edition, Merrow Publishing Co., Durham, England, 1984, p.194.
- Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990
- Rosalie Rosso King, Textile Identification, Conservation, and Preservation, Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: Nylon. Retrieved May 25, 2003.
- Website: www.nswpmith.com.au/historyofplastics.html